Integrated assessment of heavy metal pollution in the surface sediments of the Laizhou Bay and the coastal waters of the Zhangzi Island, China: comparison among typical marine sediment quality indices
- PMID: 24709993
- PMCID: PMC3978014
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0094145
Integrated assessment of heavy metal pollution in the surface sediments of the Laizhou Bay and the coastal waters of the Zhangzi Island, China: comparison among typical marine sediment quality indices
Abstract
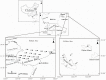
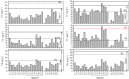
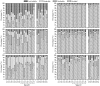
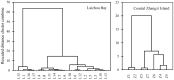
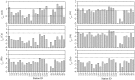
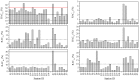
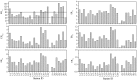
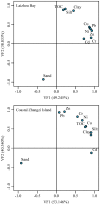
The total concentrations and chemical forms of heavy metals (Cd, Cr, Cu, Ni, Pb and Zn) in the surface sediments of the Laizhou Bay and the surrounding marine area of the Zhangzi Island (hereafter referred to as Zhangzi Island for short) were obtained and multiple indices and guidelines were applied to assess their contamination and ecological risks. The sedimentary conditions were fine in both of the two studied areas according to the marine sediment quality of China. Whereas the probable effects level guideline suggested that Ni might cause adverse biological effects to occur frequently in some sites. All indices used suggested that Cd posed the highest environmental risk in both the Laizhou Bay and the Zhangzi Island, though Cd may unlikely be harmful to human and ecological health due to the very low total concentrations. The enrichment factor (EF) showed that a substantial portion of Cr was delivered from anthropogenic sources, whereas the risk assessment code (RAC) indicated that most Cr was in an inactive state that it may not have any adverse effect either. Moreover, the results of EF and geoaccumulation index were consistent with the trend of the total metal concentrations except for Cd, while the results of RAC and potential ecological risk factor did not follow the same trend of their corresponding total metal concentrations. We also evaluated the effects of using different indices to assess the environmental impact of these heavy metals.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



References
-
- Prica M, Dalmacija B, Rončević S, Krčmar D, Bečelić M (2008) A comparison of sediment quality results with acid volatile sulfide (AVS) and simultaneously extracted metals (SEM) ratio in Vojvodina (Serbia) sediments. Sci Total Environ 389: 235–244. - PubMed
-
- Yang YQ, Chen FR, Zhang L, Liu JS, Wu SJ, et al. (2012) Comprehensive assessment of heavy metal contamination in sediment of the Pearl River Estuary and adjacent shelf. Mar Pollut Bull 64: 1947–1955. - PubMed
-
- Gao XL, Chen CTA (2012) Heavy metal pollution status in surface sediments of the coastal Bohai Bay. Water Res 46: 1901–1911. - PubMed
-
- Gao XL, Zhou FX, Chen CTA (2014) Pollution status of the Bohai Sea, China: An overview of the environmental quality assessment related trace metals. Environ Int 62: 12–30. - PubMed
-
- Varol M (2011) Assessment of heavy metal contamination in sediments of the Tigris River (Turkey) using pollution indices and multivariate statistical techniques. J Hazard Mater 195: 355–364. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

