Ultra-sensitive liquid biopsy of circulating extracellular vesicles using ExoScreen
- PMID: 24710016
- PMCID: PMC3988821
- DOI: 10.1038/ncomms4591
Ultra-sensitive liquid biopsy of circulating extracellular vesicles using ExoScreen
Abstract
Cancer cells secrete small membranous extracellular vesicles (EVs) into their microenvironment and circulation. Although their potential as cancer biomarkers has been promising, the identification and quantification of EVs in clinical samples remains challenging. Here we describe a sensitive and rapid analytical technique for profiling circulating EVs directly from blood samples of patients with colorectal cancer. EVs are captured by two types of antibodies and are detected by photosensitizer-beads, which enables us to detect cancer-derived EVs without a purification step. We also show that circulating EVs can be used for detection of colorectal cancer using the antigen CD147, which is embedded in cancer-linked EVs. This work describes a new liquid biopsy technique to sensitively detect disease-specific circulating EVs and provides perspectives in translational medicine from the standpoint of diagnosis and therapy.
Figures

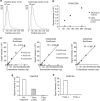
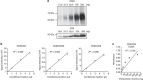
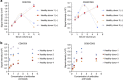
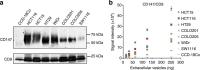
References
-
- Iero M. et al.. Tumour-released exosomes and their implications in cancer immunity. Cell Death Differ. 15, 80–88 (2008). - PubMed
-
- Webber J., Steadman R., Mason M. D., Tabi Z. & Clayton A. Cancer exosomes trigger fibroblast to myofibroblast differentiation. Cancer Res. 70, 9621–9630 (2010). - PubMed
-
- Al-Nedawi K. et al.. Intercellular transfer of the oncogenic receptor EGFRvIII by microvesicles derived from tumour cells. Nat. Cell Biol. 10, 619–624 (2008). - PubMed
-
- Taylor D. D. & Gercel-Taylor C. MicroRNA signatures of tumor-derived exosomes as diagnostic biomarkers of ovarian cancer. Gynecol. Oncol. 110, 13–21 (2008). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

