A Global Expression Switch Marks Pachytene Initiation during Mouse Male Meiosis
- PMID: 24710097
- PMCID: PMC3966219
- DOI: 10.3390/genes1030469
A Global Expression Switch Marks Pachytene Initiation during Mouse Male Meiosis
Abstract
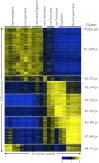
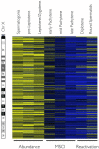
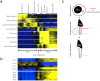
Male spermatogenesis is an essential and complex process necessary to gain totipotency and allow a whole new organism to develop upon fertilization. While single-gene based studies have provided insights into the mechanisms underlying spermatogenesis, detailed global profiling of all the key meiotic stages is required to fully define these processes. Here, by isolating highly enriched mouse meiotic cell populations, we have generated a comprehensive gene expression atlas of mammalian meiosis. Our data define unique signatures for the specific stages of meiosis, including global chromosome X inactivation and reactivation. The data also reveal profound switches in global gene expression at the initiation of pachynema that are reminiscent of the commitment to meiosis observed in budding yeast. Overall, this meiotic atlas provides an exhaustive blueprint and resource for mammalian gametogenesis and meiosis.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Transcriptome analysis of highly purified mouse spermatogenic cell populations: gene expression signatures switch from meiotic-to postmeiotic-related processes at pachytene stage.BMC Genomics. 2016 Apr 19;17:294. doi: 10.1186/s12864-016-2618-1. BMC Genomics. 2016. PMID: 27094866 Free PMC article.
-
The meiotic-mitotic initiation switch in budding yeast maintains its function robustly against sensitive parameter perturbations.Biosystems. 2014 Oct;124:61-74. doi: 10.1016/j.biosystems.2014.09.003. Epub 2014 Sep 4. Biosystems. 2014. PMID: 25195149
-
Silencing of X-Linked MicroRNAs by Meiotic Sex Chromosome Inactivation.PLoS Genet. 2015 Oct 28;11(10):e1005461. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1005461. eCollection 2015 Oct. PLoS Genet. 2015. PMID: 26509798 Free PMC article.
-
Sex-chromosome pairing and activity during mammalian meiosis.Bioessays. 1992 Dec;14(12):817-22. doi: 10.1002/bies.950141205. Bioessays. 1992. PMID: 1365897 Review.
-
YY1 and CP2c in Unidirectional Spermatogenesis and Stemness.Dev Reprod. 2020 Dec;24(4):249-262. doi: 10.12717/DR.2020.24.4.249. Epub 2020 Dec 31. Dev Reprod. 2020. PMID: 33537512 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Regulatory complexity revealed by integrated cytological and RNA-seq analyses of meiotic substages in mouse spermatocytes.BMC Genomics. 2016 Aug 12;17(1):628. doi: 10.1186/s12864-016-2865-1. BMC Genomics. 2016. PMID: 27519264 Free PMC article.
-
Uncoupling of transcriptomic and cytological differentiation in mouse spermatocytes with impaired meiosis.Mol Biol Cell. 2019 Mar 1;30(5):717-728. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E18-10-0681. Epub 2019 Jan 16. Mol Biol Cell. 2019. PMID: 30649999 Free PMC article.
-
Integrated transcriptome analysis of mouse spermatogenesis.BMC Genomics. 2014 Jan 18;15:39. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-15-39. BMC Genomics. 2014. PMID: 24438502 Free PMC article.
-
Optimized flow cytometry isolation of murine spermatocytes.Cytometry A. 2014 Jun;85(6):556-65. doi: 10.1002/cyto.a.22463. Epub 2014 Mar 24. Cytometry A. 2014. PMID: 24664803 Free PMC article.
-
Variation in human recombination rates and its genetic determinants.PLoS One. 2011;6(6):e20321. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0020321. Epub 2011 Jun 17. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21698098 Free PMC article.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

