Synaptonemal complex length variation in wild-type male mice
- PMID: 24710100
- PMCID: PMC3966217
- DOI: 10.3390/genes1030505
Synaptonemal complex length variation in wild-type male mice
Abstract
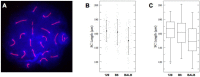
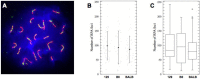
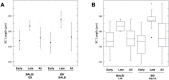
Meiosis yields haploid gametes following two successive divisions of a germ cell in the absence of intervening DNA replication. Balanced segregation of homologous chromosomes in Meiosis I is aided by a proteinaceous structure, the synaptonemal complex (SC). The objective of this study was to determine total average autosomal SC lengths in spermatocytes in three commonly used mouse strains (129S4/SvJae, C57BL/6J, and BALB/c). Our experiments revealed that the total autosomal SC length in BALB/c spermatocytes is 9% shorter than in the two other strains. Shorter SCs are also observed in spermatocytes of (BALB/c × 129S4/SvJae) and (C57BL/6J × BALB/c) F1 hybrids suggesting a genetic basis of SC length regulation. Along these lines, we studied expression of a selected group of genes implicated in meiotic chromosome architecture. We found that BALB/c testes express up to 6-fold less of Rec8 mRNA and 4-fold less of REC8 protein. These results suggest that the mechanism that defines the SC length operates via a REC8‑dependent process. Finally, our results demonstrate that genetic background can have an effect on meiotic studies in mice.
Figures

References
-
- Costa Y., Cooke H.J. Dissecting the mammalian synaptonemal complex using targeted mutations. Chromosome Res. 2007;15:579–589. - PubMed
-
- Moses M.J. Structure and function of the synaptonemal complex. Genetics. 1969;61:41–51. - PubMed
-
- Moses M.J., Dresser M.E., Poorman P.A. Composition and role of the synaptonemal complex. Symp. Soc. Exp. Biol. 1984;38:245–270. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

