Prospects and limitations of using endogenous neural stem cells for brain regeneration
- PMID: 24710140
- PMCID: PMC3924842
- DOI: 10.3390/genes2010107
Prospects and limitations of using endogenous neural stem cells for brain regeneration
Abstract
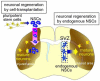
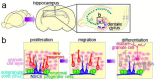
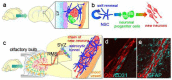
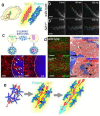
Neural stem cells (NSCs) are capable of producing a variety of neural cell types, and are indispensable for the development of the mammalian brain. NSCs can be induced in vitro from pluripotent stem cells, including embryonic stem cells and induced-pluripotent stem cells. Although the transplantation of these exogenous NSCs is a potential strategy for improving presently untreatable neurological conditions, there are several obstacles to its implementation, including tumorigenic, immunological, and ethical problems. Recent studies have revealed that NSCs also reside in the adult brain. The endogenous NSCs are activated in response to disease or trauma, and produce new neurons and glia, suggesting they have the potential to regenerate damaged brain tissue while avoiding the above-mentioned problems. Here we present an overview of the possibility and limitations of using endogenous NSCs in regenerative medicine.
Figures


References
-
- Gerrard L., Rodgers L., Cui W. Differentiation of human embryonic stem cells to neural lineages in adherent culture by blocking bone morphogenetic protein signaling. Stem Cells. 2005;23:1234–1241. - PubMed
-
- Okada Y., Matsumoto A., Shimazaki T., Enoki R., Koizumi A., Ishii S., Itoyama Y., Sobue G., Okano H. Spatiotemporal recapitulation of central nervous system development by murine embryonic stem cell-derived neural stem/progenitor cells. Stem Cells. 2008;26:3086–3098. - PubMed
-
- Takahashi K., Yamanaka S. Induction of pluripotent stem cells from mouse embryonic and adult fibroblast cultures by defined factors. Cell. 2006;126(4):663–676. - PubMed
-
- Yamanaka S. Strategies and new developments in the generation of patient-specific pluripotent stem cells. Cell Stem Cell. 2007;1(1):39–49. - PubMed
-
- Zhang S.C., Wernig M., Duncan I.D., Brustle O., Thomson J.A. In vitro differentiation of transplantable neural precursors from human embryonic stem cells. Nat. Biotechnol. 2001;19(12):1129–1133. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

