Simultaneous Detection of Antigen-Specific IgG- and IgM-Secreting Cells with a B Cell Fluorospot Assay
- PMID: 24710360
- PMCID: PMC3972644
- DOI: 10.3390/cells1010015
Simultaneous Detection of Antigen-Specific IgG- and IgM-Secreting Cells with a B Cell Fluorospot Assay
Abstract
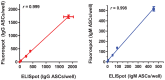
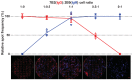
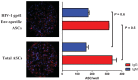
The traditional enzyme-linked immunospot (ELISpot) assay is the gold standard for the enumeration of antigen-specific B cells. Since B cell availability from biological samples is often limited, either because of sample size/volume or the need of performing multiple analyses on the same sample, the implementation of ELISpot assay formats that allow the simultaneous detection of multiple antibody types is desirable. While dual-color ELISpot assays have been described, technical complexities have so far prevented their wide utilization as well as further expansion of their multicolor capability. An attractive solution is to replace the chromogenic reaction of the traditional ELISpot assay with a fluorescent detection system (fluorospot assay). Fluorospot assays using fluorophore-conjugated secondary antibodies in conjunction with fluorescence enhancers, FITC/anti-FITC and biotin/avidin amplification systems and dedicated equipment for spot detection have been developed to enumerate T-cells secreting two or three specific cytokines and, more recently, IgG and IgA antibody-secreting cells (ASCs). We hereby report a method for a multiplex B cell fluorospot assay that utilizes quantum-dot nanocrystals as reporters without further amplification systems or need of dedicated equipment. With this method we simultaneously enumerated HIV-1 gp41 envelope glycoprotein-specific IgG and IgM antibody-secreting cells with sensitivity comparable to that of the traditional ELISpot assay.
Figures
Similar articles
-
An antigen-specific, four-color, B-cell FluoroSpot assay utilizing tagged antigens for detection.J Immunol Methods. 2016 Jun;433:23-30. doi: 10.1016/j.jim.2016.02.020. Epub 2016 Feb 27. J Immunol Methods. 2016. PMID: 26930550
-
Comparison of ELISpot and FluoroSpot in the Analysis of Swine Flu-Specific IgG and IgA Secretion by in Vivo Activated Human B Cells.Cells. 2012 Apr 20;1(2):27-34. doi: 10.3390/cells1020027. Cells. 2012. PMID: 24710411 Free PMC article.
-
Detection and Enumeration of Cytokine-Secreting Cells by FluoroSpot.Methods Mol Biol. 2022;2386:81-99. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-1771-7_6. Methods Mol Biol. 2022. PMID: 34766266
-
Multiplexing T- and B-Cell FLUOROSPOT Assays: Experimental Validation of the Multi-Color ImmunoSpot® Software Based on Center of Mass Distance Algorithm.Methods Mol Biol. 2018;1808:95-113. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-8567-8_9. Methods Mol Biol. 2018. PMID: 29956177
-
The Importance of Monitoring Antigen-Specific Memory B Cells, and How ImmunoSpot Assays Are Suitable for This Task.Cells. 2025 Feb 5;14(3):223. doi: 10.3390/cells14030223. Cells. 2025. PMID: 39937014 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Characterization of Thymus-dependent and Thymus-independent Immunoglobulin Isotype Responses in Mice Using Enzyme-linked Immunosorbent Assay.J Vis Exp. 2018 Sep 7;(139):57843. doi: 10.3791/57843. J Vis Exp. 2018. PMID: 30247482 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Tuaillon E., Tabaa Y.A., Petitjean G., Huguet M.F., Pajeaux G., Fondere J.M., Ponseille B., Ducos J., Blanc P., Vendrell J.P. Detection of memory B lymphocytes specific to hepatitis B virus (HBV) surface antigen (HBsAg) from HBsAg-vaccinated or HBV-immunized subjects by ELISPOT assay. J. Immunol. Methods. 2006;315:144–152. doi: 10.1016/j.jim.2006.07.016. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bonsignori M., Moody M.A., Parks R.J., Holl T.M., Kelsoe G., Hicks C.B., Vandergrift N., Tomaras G.D., Haynes B.F. HIV-1 envelope induces memory B cell responses that correlate with plasma antibody levels after envelope gp120 protein vaccination or HIV-1 infection. J. Immunol. 2009;183:2708–2717. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.0901068. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

