Radiographic loss of contact between radial head fracture fragments is moderately reliable
- PMID: 24711128
- PMCID: PMC4048410
- DOI: 10.1007/s11999-014-3592-z
Radiographic loss of contact between radial head fracture fragments is moderately reliable
Abstract
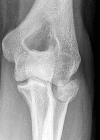
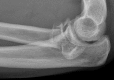
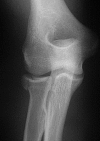
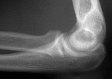
Background: Loss of contact between radial head fracture fragments is strongly associated with other elbow or forearm injuries. If this finding has adequate interobserver reliability, it could help examiners identify and treat associated ligament injuries and fractures (eg, forearm interosseous ligament injury or elbow dislocation).
Questions/purposes: (1) What is the interobserver agreement on radiographic loss of contact between radial head fracture fragments? (2) Are there factors associated with the observer such as location of practice or subspecialization that increase interobserver reliability?
Methods: Fully trained practicing orthopaedic and trauma surgeons from around the world evaluated 27 anteroposterior and lateral radiographs of radial head fractures on a web-based platform for the following characteristics: (1) loss of contact between at least one radial head fracture fragment and the remaining radial head and neck; (2) a gap between fragments of 2 mm or greater; (3) anticipated fracture instability (mobility) on operative exposure; (4) anticipated associated ligament injuries; and (5) recommendation for treatment. Agreement among observers was measured using the multirater kappa measure. Kappas for various observer characteristics were compared using 95% confidence intervals.
Results: The overall interobserver agreement was moderate (range, 0.49-0.55) for each question except associated ligament injury, which was fair (0.33). Shoulder and elbow surgeons had substantial agreement (range, 0.51-0.61) in many areas, but kappas were generally in the moderate range (0.41-0.59) based on number of years in practice, radial head fractures treated per year, and trainee supervision.
Conclusions: Radiographic signs of radial head fracture instability such as loss of contact have moderate reliability. This characteristic seems clinically useful, because loss of contact between at least one radial head fracture fragment and the remaining radial head and neck is strongly associated with associated ligament injury or other fractures.
Level of evidence: Level III, diagnostic study. See Guidelines for Authors for a complete description of levels of evidence.
Figures
References
-
- Bernstein J, Adler LM, Blank JE, Dalsey RM, Williams GR, Iannotti JP. Evaluation of the Neer system of classification of proximal humeral fractures with computerized tomographic scans and plain radiographs. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1996;78:1371–1375. - PubMed
-
- Broberg MA, Morrey BF. Results of treatment of fracture-dislocations of the elbow. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1987;216:109–119. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

