Bosutinib efficacy and safety in chronic phase chronic myeloid leukemia after imatinib resistance or intolerance: Minimum 24-month follow-up
- PMID: 24711212
- PMCID: PMC4173127
- DOI: 10.1002/ajh.23728
Bosutinib efficacy and safety in chronic phase chronic myeloid leukemia after imatinib resistance or intolerance: Minimum 24-month follow-up
Abstract
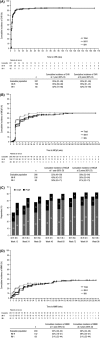
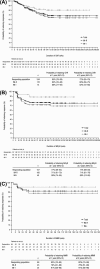
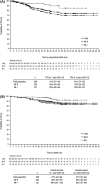
Bosutinib is an orally active, dual Src/Abl tyrosine kinase inhibitor for treatment of chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) following resistance/intolerance to prior therapy. Here, we report the data from the 2-year follow-up of a phase 1/2 open-label study evaluating the efficacy and safety of bosutinib as second-line therapy in 288 patients with chronic phase CML resistant (n = 200) or intolerant (n = 88) to imatinib. The cumulative response rates to bosutinib were as follows: 85% achieved/maintained complete hematologic response, 59% achieved/maintained major cytogenetic response (including 48% with complete cytogenetic response), and 35% achieved major molecular response. Responses were durable, with 2-year estimates of retaining response >70%. Two-year probabilities of progression-free survival and overall survival were 81% and 91%, respectively. The most common toxicities were primarily gastrointestinal adverse events (diarrhea [84%], nausea [45%], vomiting [37%]), which were primarily mild to moderate, typically transient, and first occurred early during treatment. Thrombocytopenia was the most common grade 3/4 hematologic laboratory abnormality (24%). Outcomes were generally similar among imatinib-resistant and imatinib-intolerant patients and did not differ with age. The longer-term results of the present analysis confirm that bosutinib is an effective and tolerable second-line therapy for patients with imatinib-resistant or imatinib-intolerant chronic phase CML. ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT00261846.
© 2014 The Authors American Journal of Hematology Published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Safety and efficacy of bosutinib (SKI-606) in chronic phase Philadelphia chromosome-positive chronic myeloid leukemia patients with resistance or intolerance to imatinib.Blood. 2011 Oct 27;118(17):4567-76. doi: 10.1182/blood-2011-05-355594. Epub 2011 Aug 24. Blood. 2011. PMID: 21865346 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Bosutinib versus imatinib in newly diagnosed chronic-phase chronic myeloid leukaemia: results from the 24-month follow-up of the BELA trial.Br J Haematol. 2015 Jan;168(1):69-81. doi: 10.1111/bjh.13108. Epub 2014 Sep 8. Br J Haematol. 2015. PMID: 25196702 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Bosutinib safety and management of toxicity in leukemia patients with resistance or intolerance to imatinib and other tyrosine kinase inhibitors.Blood. 2014 Feb 27;123(9):1309-18. doi: 10.1182/blood-2013-07-513937. Epub 2013 Dec 17. Blood. 2014. PMID: 24345751 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Bosutinib for the treatment of chronic myeloid leukemia.Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2015 Mar 15;72(6):439-47. doi: 10.2146/ajhp140221. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2015. PMID: 25736937 Review.
-
Bosutinib: a review of its use in patients with Philadelphia chromosome-positive chronic myelogenous leukemia.BioDrugs. 2014 Feb;28(1):107-20. doi: 10.1007/s40259-013-0082-x. BioDrugs. 2014. PMID: 24420842 Review.
Cited by
-
A phase 3, open-label, randomized study of asciminib, a STAMP inhibitor, vs bosutinib in CML after 2 or more prior TKIs.Blood. 2021 Nov 25;138(21):2031-2041. doi: 10.1182/blood.2020009984. Blood. 2021. PMID: 34407542 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Bosutinib versus Placebo for Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease.J Am Soc Nephrol. 2017 Nov;28(11):3404-3413. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2016111232. Epub 2017 Aug 24. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2017. PMID: 28838955 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Bosutinib-Induced Pleural Effusion-Class Effect and Cross-Intolerance to All Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors.Hematol Rep. 2025 Jan 31;17(1):7. doi: 10.3390/hematolrep17010007. Hematol Rep. 2025. PMID: 39997355 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting EZH2 for cancer therapy: progress and perspective.Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2015;16(6):559-70. doi: 10.2174/1389203716666150409100233. Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2015. PMID: 25854924 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pharmacology of tyrosine kinase inhibitors in chronic myeloid leukemia; a clinician's perspective.Daru. 2020 Jun;28(1):371-385. doi: 10.1007/s40199-019-00321-z. Epub 2020 Jan 3. Daru. 2020. PMID: 31900888 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Faderl S, Talpaz M, Estrov Z, et al. The biology of chronic myeloid leukemia. N Engl J Med. 1999;341(3):164–172. - PubMed
-
- National Comprehensive Cancer Network. NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology™. Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia. Version 3.2013. Available at: http://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/PDF/cml.pdf. Accessed December 5, 2013.
-
- Diamond JM, Melo JV. Mechanisms of resistance to BCR-ABL kinase inhibitors. Leuk Lymphoma. 2011;52(Suppl. 1):12–22. - PubMed
-
- Hochhaus A, Baccarani M, Deininger M, et al. Dasatinib induces durable cytogenetic responses in patients with chronic myelogenous leukemia in chronic phase with resistance or intolerance to imatinib. Leukemia. 2008;22(6):1200–1206. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
