Giant myoepithelioma of the soft palate
- PMID: 24711949
- PMCID: PMC3965919
- DOI: 10.1155/2014/561259
Giant myoepithelioma of the soft palate
Abstract
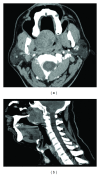
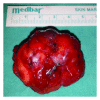
Myoepitheliomas are benign salivary gland tumors and account for less than 1% of all salivary gland tumors. They are usually located in the parotid gland. The soft palate is very rare affected site. The differential diagnosis of myoepitheliomas should include reactive and neoplastic lesions. The treatment of myoepitheliomas is complete removal of the tumor. Herein, we report a case with giant myoepithelioma of the soft palate, reviewing the related literature.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Clear cell myoepithelioma of palate with emphasis on clinical and histological differential diagnosis.Clin Pract. 2014 May 7;4(1):628. doi: 10.4081/cp.2014.628. eCollection 2014 Mar 27. Clin Pract. 2014. PMID: 24847433 Free PMC article.
-
Myoepithelioma of the Soft Palate.J Craniofac Surg. 2018 May;29(3):e217-e219. doi: 10.1097/SCS.0000000000004096. J Craniofac Surg. 2018. PMID: 29077683
-
Palatal plasmacytoid myoepithelioma.Adv Biomed Res. 2012;1:78. doi: 10.4103/2277-9175.102985. Epub 2012 Oct 31. Adv Biomed Res. 2012. PMID: 23326808 Free PMC article.
-
Plasmacytoid myoepithelioma of the soft palate: a review of the literature and report of a case with immunohistochemical findings.Kulak Burun Bogaz Ihtis Derg. 2005;14(5-6):127-30. Kulak Burun Bogaz Ihtis Derg. 2005. PMID: 16340282 Review.
-
Plasmacytoid myoepithelioma of palate: three rare cases and literature review.J Laryngol Otol. 2007 Sep;121(9):e13. doi: 10.1017/S002221510700000X. Epub 2007 Jul 19. J Laryngol Otol. 2007. PMID: 17640425 Review.
Cited by
-
Myoepithelioma of the Parotid Gland: A Case Report with Review of the Literature and Classic Histopathology.Case Rep Otolaryngol. 2017;2017:6036179. doi: 10.1155/2017/6036179. Epub 2017 Aug 16. Case Rep Otolaryngol. 2017. PMID: 28900549 Free PMC article.
-
Recurrent Myoepithelioma Treated by Palatal and Piriform Apertural Approaches.Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2015 Sep 8;3(9):e508. doi: 10.1097/GOX.0000000000000491. eCollection 2015 Sep. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2015. PMID: 26495221 Free PMC article.
-
Unveiling rarity: Myoepithelioma in the minor salivary gland of buccal mucosa - A case report.Int J Surg Case Rep. 2024 Jul;120:109849. doi: 10.1016/j.ijscr.2024.109849. Epub 2024 Jun 1. Int J Surg Case Rep. 2024. PMID: 38875824 Free PMC article.
-
Benign myoepithelioma of the soft palate: an unusual clinical entity.BMJ Case Rep. 2021 Jun 29;14(6):e240384. doi: 10.1136/bcr-2020-240384. BMJ Case Rep. 2021. PMID: 34187791 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Testa D, Galera F, Insabato L, Vassallo A, Mesolella M, Galli V. Submandibular gland myoepithelioma. Acta Oto-Laryngologica. 2005;125(6):664–666. - PubMed
-
- da Cruz Perez DE, Lopes MA, de Almeida OP, Jorge J, Kowalski LP. Plasmacytoid myoepithelioma of the palate in a child. International Journal of Paediatric Dentistry. 2007;17(3):223–227. - PubMed
-
- Yaman H, Gerek M, Tosun F, Deveci S, Kiliç E, Arslan HH. Myoepithelioma of the parotid gland in a child: a case report. Journal of Pediatric Surgery. 2010;45(7):e5–e7. - PubMed
-
- Açikalin MF, Paşaoğlu O, Cakli H, Ciftçi E. Plasmacytoid myoepithelioma of the soft palate: a review of the literature and report of a case with immunohistochemical findings. Kulak Burun Boğaz İhtisas Dergisi. 2005;14(5-6):127–130. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

