Treatment with lenalidomide induces immunoactivating and counter-regulatory immunosuppressive changes in myeloma patients
- PMID: 24712857
- PMCID: PMC4226595
- DOI: 10.1111/cei.12343
Treatment with lenalidomide induces immunoactivating and counter-regulatory immunosuppressive changes in myeloma patients
Abstract
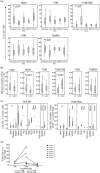
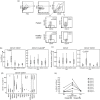
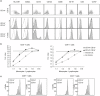
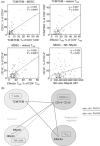
Lenalidomide activates the immune system, but the exact immunomodulatory mechanisms of lenalidomide in vivo are poorly defined. In an observational study we assessed the impact of lenalidomide on different populations of immune cells in multiple myeloma patients. Lenalidomide therapy was associated with increased amounts of a CD8(+) T cell subset, phenotypically staged between classical central memory T cells (TCM) and effector memory T cells (TEM), consequently termed TCM/TEM. The moderate expression of perforin/granzyme and phenotypical profile of these cells identifies them as not yet terminally differentiated, which makes them promising candidates for the anti-tumour response. In addition, lenalidomide-treated patients showed higher abundance of CD14(+) myeloid cells co-expressing CD15. This population was able to inhibit both CD4(+) and CD8(+) T cell proliferation in vitro and could thus be defined as a so far undescribed novel myeloid-derived suppressor cell (MDSC) subtype. We observed a striking correlation between levels of TCM/TEM, mature regulatory T cells (T(regs)) and CD14(+) CD15(+) MDSCs. In summary, lenalidomide induces both activating and inhibitory components of the immune system, indicating the existence of potential counter-regulatory mechanisms. These findings provide new insights into the immunomodulatory action of lenalidomide.
Keywords: MDSCs; T cells; immunoregulation; lenalidomide; multiple myeloma.
© 2014 British Society for Immunology.
Figures

References
-
- Cook G, Campbell JD, Carr CE, Boyd KS, Franklin IM. Transforming growth factor beta from multiple myeloma cells inhibits proliferation and IL-2 responsiveness in T lymphocytes. J Leukoc Biol. 1999;66:981–988. - PubMed
-
- Liu J, Hamrouni A, Wolowiec D, et al. Plasma cells from multiple myeloma patients express B7-H1 (PD-L1) and increase expression after stimulation with IFN-{gamma} and TLR ligands via a MyD88-, TRAF6-, and MEK-dependent pathway. Blood. 2007;110:296–304. - PubMed
-
- Brown RD, Pope B, Murray A, et al. Dendritic cells from patients with myeloma are numerically normal but functionally defective as they fail to up-regulate CD80 (B7-1) expression after huCD40LT stimulation because of inhibition by transforming growth factor-beta1 and interleukin-10. Blood. 2001;98:2992–2998. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

