Effect of oxygenation and temperature on glucose-xylose fermentation in Kluyveromyces marxianus CBS712 strain
- PMID: 24712908
- PMCID: PMC3991920
- DOI: 10.1186/1475-2859-13-51
Effect of oxygenation and temperature on glucose-xylose fermentation in Kluyveromyces marxianus CBS712 strain
Abstract
Background: The yeast Kluyveromyces marxianus features specific traits that render it attractive for industrial applications. These include production of ethanol which, together with thermotolerance and the ability to grow with a high specific growth rate on a wide range of substrates, could make it an alternative to Saccharomyces cerevisiae as an ethanol producer. However, its ability to co-ferment C5 and C6 sugars under oxygen-limited conditions is far from being fully characterized.
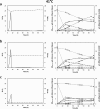
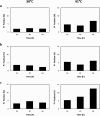
Results: In the present study, K. marxianus CBS712 strain was cultivated in defined medium with glucose and xylose as carbon source. Ethanol fermentation and sugar consumption of CBS712 were investigated under different oxygen supplies (1.75%, 11.00% and 20.95% of O2) and different temperatures (30°C and 41°C). By decreasing oxygen supply, independently from the temperature, both biomass production as well as sugar utilization rate were progressively reduced. In all the tested conditions xylose consumption followed glucose exhaustion. Therefore, xylose metabolism was mainly affected by oxygen depletion. Loss in cell viability cannot explain the decrease in sugar consumption rates, as demonstrated by single cell analyses, while cofactor imbalance is commonly considered as the main cause of impairment of the xylose reductase (KmXR) - xylitol dehydrogenase (KmXDH) pathway. Remarkably, when these enzyme activities were assayed in vitro, a significant decrease was observed together with oxygen depletion, not ascribed to reduced transcription of the corresponding genes.
Conclusions: In the present study both oxygen supply and temperature were shown to be key parameters affecting the fermentation capability of sugars in the K. marxianus CBS712 strain. In particular, a direct correlation was observed between the decreased efficiency to consume xylose with the reduced specific activity of the two main enzymes (KmXR and KmXDH) involved in its catabolism. These data suggest that, in addition to the impairment of the oxidoreductive pathway being determined by the cofactor imbalance, post-transcriptional and/or post-translational regulation of the pathway enzymes contributes to the efficiency of xylose catabolism in micro-aerobic conditions. Overall, the presented work provides novel information on the fermentation capability of the CBS712 strain that is currently considered as the reference strain of the genus K. marxianus.
Figures


References
-
- Lane MM, Morrissey JP. Kluyveromyces marxianus: A yeast emerging from its sister’s shadow. Fungal Biol Rev. 2010;24:7–26.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

