Chronic kidney disease and associated mortality after liver transplantation--a time-dependent analysis using measured glomerular filtration rate
- PMID: 24713190
- PMCID: PMC4160310
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2014.03.034
Chronic kidney disease and associated mortality after liver transplantation--a time-dependent analysis using measured glomerular filtration rate
Abstract
Background & aims: The accuracy of creatinine-based estimated GFR (eGFR) in assessing the prevalence of chronic kidney disease (CKD) and associated mortality after liver transplantation (LTx) is unknown. Using measured GFR (mGFR) by iothalamate clearance, we determined the prevalence of the entire spectrum of renal dysfunction and the impact of CKD on mortality after LTx.
Methods: A database that prospectively tracks all LTx recipients at this academic transplant program from 1985 to 2012 was queried to identify all adult primary LTx recipients. Our post-LTx protocol incorporates GFR measurement by iothalamate clearance at regular intervals. A multistate model was used to assess the prevalence of CKD, kidney transplant, and death after LTx. Time-dependent Cox regression analysis was performed to evaluate the impact of mGFR and eGFR changes on survival.
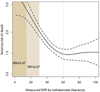
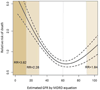
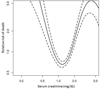
Results: A total of 1211 transplant recipients were included. At the time of LTx, the median age was 54 years, 60% were male and 86% were Caucasian. At 25 years after LTx, 54% of patients died, 9% underwent kidney transplantation, whereas 7%, 21%, and 18% had mGFR >60, 59-30, and <30 ml/min/1.73 m(2) respectively. The risk of death increased when mGFR decreased below 30 ml/min/1.73 m(2): HR = 2.67 (95% CI = 1.80-3.96) for GFR = 29-15 ml/min/1.73 m(2) and HR = 5.47 (95% CI = 3.10-9.65) for GFR <15 ml/min/1.73 m(2). Compared to mGFR, eGFR underestimated mortality risk in LTx recipients with an eGFR of 30-90 ml/min/1.73 m(2).
Conclusions: An overwhelming majority of LTx recipients develop CKD. The risk of death increases exponentially when GFR <30 ml/min/1.73 m(2). Creatinine-based eGFR underestimates the mortality risk in a large proportion of patients.
Keywords: Iothalamate clearance; Outcomes; Prevalence; Renal failure.
Copyright © 2014 European Association for the Study of the Liver. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Comment in
-
Chronic kidney disease: a major concern in liver transplantation in the XXI century.J Hepatol. 2014 Aug;61(2):196-7. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2014.05.011. Epub 2014 May 15. J Hepatol. 2014. PMID: 24845611 No abstract available.
-
Chronic kidney disease after liver transplantation.J Hepatol. 2015 Jan;62(1):243-4. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2014.08.054. Epub 2014 Sep 28. J Hepatol. 2015. PMID: 25263005 No abstract available.
-
Reply to: "Chronic kidney disease after liver transplantation".J Hepatol. 2015 Jan;62(1):244-5. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2014.09.021. Epub 2014 Sep 30. J Hepatol. 2015. PMID: 25278355 No abstract available.
-
Reply to: "Chronic kidney disease (CKD) and NAFLD: time for awareness and screening".J Hepatol. 2015 Apr;62(4):984-5. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2014.12.019. Epub 2014 Dec 18. J Hepatol. 2015. PMID: 25529624 No abstract available.
-
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) and NAFLD: time for awareness and screening.J Hepatol. 2015 Apr;62(4):983-4. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2014.11.044. Epub 2014 Dec 18. J Hepatol. 2015. PMID: 25529627 No abstract available.
References
-
- Jain A, Singhal A, Fontes P, Mazariegos G, DeVera ME, Cacciarelli T, et al. One thousand consecutive primary liver transplants under tacrolimus immunosuppression: a 17- to 20-year longitudinal follow-up. Transplantation. 2011;91:1025–1030. - PubMed
-
- Kim JY, Akalin E, Dikman S, Gagliardi R, Schiano T, Bromberg J, et al. The variable pathology of kidney disease after liver transplantation. Transplantation. 2010;89:215–221. - PubMed
-
- McGuire BM, Julian BA, Bynon JS, Jr, Cook WJ, King SJ, Curtis JJ, et al. Brief communication: Glomerulonephritis in patients with hepatitis C cirrhosis undergoing liver transplantation. Annals of internal medicine. 2006;144:735–741. - PubMed
-
- Pillebout E, Nochy D, Hill G, Conti F, Antoine C, Calmus Y, et al. Renal histopathological lesions after orthotopic liver transplantation (OLT) Am J Transplant. 2005;5:1120–1129. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

