The dynamic epitranscriptome: N6-methyladenosine and gene expression control
- PMID: 24713629
- PMCID: PMC4393108
- DOI: 10.1038/nrm3785
The dynamic epitranscriptome: N6-methyladenosine and gene expression control
Abstract
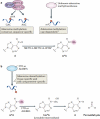
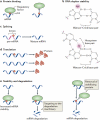
N(6)-methyladenosine (m(6)A) is a modified base that has long been known to be present in non-coding RNAs, ribosomal RNA, polyadenylated RNA and at least one mammalian mRNA. However, our understanding of the prevalence of this modification has been fundamentally redefined by transcriptome-wide m(6)A mapping studies, which have shown that m(6)A is present in a large subset of the transcriptome in specific regions of mRNA. This suggests that mRNA may undergo post-transcriptional methylation to regulate its fate and function, which is analogous to methyl modifications in DNA. Thus, the pattern of methylation constitutes an mRNA 'epitranscriptome'. The identification of adenosine methyltransferases ('writers'), m(6)A demethylating enzymes ('erasers') and m(6)A-binding proteins ('readers') is helping to define cellular pathways for the post-transcriptional regulation of mRNAs.
Figures

References
-
- Lewis JD, et al. Purification, sequence, and cellular localization of a novel chromosomal protein that binds to methylated DNA. Cell. 1992;69:905–14. - PubMed
-
- Pawson T, Scott JD. Protein phosphorylation in signaling--50 years and counting. Trends Biochem Sci. 2005;30:286–90. - PubMed
-
- Meyer KD, et al. Comprehensive analysis of mRNA methylation reveals enrichment in 3' UTRs and near stop codons. Cell. 2012;149:1635–46. [Provides the first demonstration that m6A is a widespread modification in mammalian mRNAs and reveals that m6A is highly enriched surrounding stop codons and in UTRs. Also identifies many methylated noncoding RNAs which were not previously known to contain m6A.] - PMC - PubMed
-
- Dominissini D, et al. Topology of the human and mouse m6A RNA methylomes revealed by m6A-seq. Nature. 2012;485:201–6. [Demonstrates, together with reference 3, that m6A is a pervasive feature of the transcriptome which exhibits a unique distribution within mRNAs. Identifies YTHDF2-3 and HuR as potential m6A binding proteins.] - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

