Vascular rarefaction mediates whitening of brown fat in obesity
- PMID: 24713652
- PMCID: PMC4001539
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI71643
Vascular rarefaction mediates whitening of brown fat in obesity
Abstract
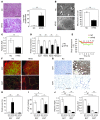
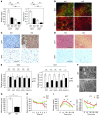
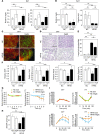
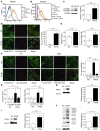
Brown adipose tissue (BAT) is a highly vascularized organ with abundant mitochondria that produce heat through uncoupled respiration. Obesity is associated with a reduction of BAT function; however, it is unknown how obesity promotes dysfunctional BAT. Here, using a murine model of diet-induced obesity, we determined that obesity causes capillary rarefaction and functional hypoxia in BAT, leading to a BAT "whitening" phenotype that is characterized by mitochondrial dysfunction, lipid droplet accumulation, and decreased expression of Vegfa. Targeted deletion of Vegfa in adipose tissue of nonobese mice resulted in BAT whitening, supporting a role for decreased vascularity in obesity-associated BAT. Conversely, introduction of VEGF-A specifically into BAT of obese mice restored vascularity, ameliorated brown adipocyte dysfunction, and improved insulin sensitivity. The capillary rarefaction in BAT that was brought about by obesity or Vegfa ablation diminished β-adrenergic signaling, increased mitochondrial ROS production, and promoted mitophagy. These data indicate that overnutrition leads to the development of a hypoxic state in BAT, causing it to whiten through mitochondrial dysfunction and loss. Furthermore, these results link obesity-associated BAT whitening to impaired systemic glucose metabolism.
Figures

References
-
- Chechi K, Carpentier AC, Richard D. Understanding the brown adipocyte as a contributor to energy homeostasis. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2013;24(8):408–420. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- UL1RR025771/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- HL081587/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR025771/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK046200/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- HL120160/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG034972/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- HL68758/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL081587/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL068758/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30DK046200/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- HL116591/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL120160/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL116591/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- AG034972/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HL007224/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

