Blood pressure control with a single-pill combination of indapamide sustained-release and amlodipine in patients with hypertension: the EFFICIENT study
- PMID: 24714044
- PMCID: PMC3979648
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0092955
Blood pressure control with a single-pill combination of indapamide sustained-release and amlodipine in patients with hypertension: the EFFICIENT study
Erratum in
- PLoS One. 2014;9(5):e98699
Abstract
Objective: Despite antihypertensive treatment, most hypertensive patients still have high blood pressure (BP), notably high systolic blood pressure (SBP). The EFFICIENT study examines the efficacy and acceptability of a single-pill combination of sustained-release (SR) indapamide, a thiazide-like diuretic, and amlodipine, a calcium channel blocker (CCB), in the management of hypertension.
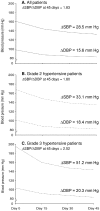
Methods: Patients who were previously uncontrolled on CCB monotherapy (BP≥140/90 mm Hg) or were previously untreated with grade 2 or 3 essential hypertension (BP≥160/100 mm Hg) received a single-pill combination tablet containing indapamide SR 1.5 mg and amlodipine 5 mg daily for 45 days, in this multicenter prospective phase 4 study. The primary outcome was mean change in BP from baseline; percentage of patients achieving BP control (BP<140/90 mm Hg) was a secondary endpoint. SBP reduction (ΔSBP) versus diastolic BP reduction (ΔDBP) was evaluated (ΔSBP/ΔDBP) from baseline to day 45. Safety and tolerability were also assessed.
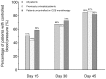
Results: Mean baseline BP of 196 patients (mean age 52.3 years) was 160.2/97.9 mm Hg. After 45 days, mean SBP decreased by 28.5 mm Hg (95% CI, 26.4 to 30.6), while diastolic BP decreased by 15.6 mm Hg (95% CI, 14.5 to 16.7). BP control (<140/90 mm Hg) was achieved in 85% patients. ΔSBP/ΔDBP was 1.82 in the overall population. Few patients (n = 3 [2%]) reported side effects, and most (n = 194 [99%]) adhered to treatment.
Conclusion: In patients who were previously uncontrolled on CCB monotherapy or untreated with grade 2 or 3 hypertension, single-pill combination indapamide SR/amlodipine reduced BP effectively--especially SBP--over 45 days, and was safe and well tolerated.
Trial registration: Clinical Trial Registry-India CTRI/2010/091/000114.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Turnbull F (2003) Effects of different blood-pressure-lowering regimens on major cardiovascular events: results of prospectively-designed overviews of randomised trials. Lancet 362: 1527–1535.. - PubMed
-
- Beckett NS, Peters R, Fletcher AE, Staessen JA, Liu L, et al. (2008) Treatment of hypertension in Patients 80 years of Age or Older. N Engl J Med 358: 1887–1898.. - PubMed
-
- Collins R, Peto R (1994) Antihypertensive drug therapy: effects on stroke and coronary heart disease. In: Swales JD, eds. Textbook of Hypertension. Oxford, UK: Blackwell Scientific Publications; 1156–1164.
-
- Mohan V, Deepa M, Farooq S, Datta M, Deepa R (2007) Prevalence, awareness and control of hypertension in Chennai–The Chennai Urban Rural Epidemiology Study (CURES-52). J Assoc Physicians India 55: 326–332.. - PubMed
-
- Tocci G, Rosei EA, Ambrosioni E, Borghi C, Ferri C, et al. (2012) Blood pressure control in Italy: analysis of clinical data from 2005–2011 surveys on hypertension. J Hypertens 30: 1065–1074.. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

