HIV monoclonal antibodies: a new opportunity to further reduce mother-to-child HIV transmission
- PMID: 24714363
- PMCID: PMC3979646
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1001616
HIV monoclonal antibodies: a new opportunity to further reduce mother-to-child HIV transmission
Abstract
Yegor Voronin and colleagues explore how monoclonal antibodies against HIV could provide a new opportunity to further reduce mother-to-child transmission of HIV and propose that new interventions should consider issues related to implementation, feasibility, and access. Please see later in the article for the Editors' Summary.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
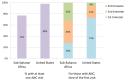
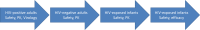
References
-
- UNAIDS (n.d.) Believe it. Do it—The Global Plan. Available: http://www.unaids.org/believeitdoit/the-global-plan.html. Accessed 8 August 2013.
-
- UNAIDS (2013) 2013 progress report on the Global Plan towards the elimination of new HIV infections among children by 2015 and keeping their mothers alive.
-
- Richman DD, Wrin T, Little SJ, Petropoulos CJ (2003) Rapid evolution of the neutralizing antibody response to HIV type 1 infection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 100: 4144–4149 doi:10.1073/pnas.0630530100 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Rollins N, Coovadia HM (2013) Breastfeeding and HIV transmission in the developing world: past, present, future. Curr Opin HIV AIDS 8: 466–472 doi:10.1097/COH.0b013e3283632ba2 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Chibwesha CJ, Giganti MJ, Putta N, Chintu N, Mulindwa J, et al. (2011) Optimal time on HAART for prevention of mother-to-child transmission of HIV. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr 58: 224–228 doi:10.1097/QAI.0b013e318229147e - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

