The functional diversity of protein lysine methylation
- PMID: 24714364
- PMCID: PMC4023394
- DOI: 10.1002/msb.134974
The functional diversity of protein lysine methylation
Abstract
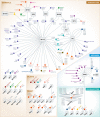
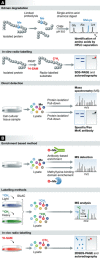
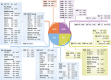
Large-scale characterization of post-translational modifications (PTMs), such as phosphorylation, acetylation and ubiquitination, has highlighted their importance in the regulation of a myriad of signaling events. While high-throughput technologies have tremendously helped cataloguing the proteins modified by these PTMs, the identification of lysine-methylated proteins, a PTM involving the transfer of one, two or three methyl groups to the ε-amine of a lysine side chain, has lagged behind. While the initial findings were focused on the methylation of histone proteins, several studies have recently identified novel non-histone lysine-methylated proteins. This review provides a compilation of all lysine methylation sites reported to date. We also present key examples showing the impact of lysine methylation and discuss the circuitries wired by this important PTM.
Figures

References
-
- Abu‐Farha M, Lanouette S, Elisma F, Tremblay V, Butson J, Figeys D, Couture J‐F (2011) Proteomic analyses of the SMYD family interactomes identify HSP90 as a novel target for SMYD2. J Mol Cell Biol 3: 301–308 - PubMed
-
- Ambler RP, Rees MW (1959) Epsilon‐N‐Methyl‐lysine in bacterial flagellar protein. Nature 184: 56–57 - PubMed
-
- Ames GF, Niakido K (1979) In vivo methylation of prokaryotic elongation factor Tu. J Biol Chem 254: 9947–9950 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

