Small interfering RNA targeting nerve growth factor alleviates allergic airway hyperresponsiveness
- PMID: 24714423
- PMCID: PMC4011123
- DOI: 10.1038/mtna.2014.11
Small interfering RNA targeting nerve growth factor alleviates allergic airway hyperresponsiveness
Abstract
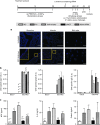
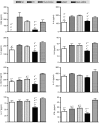
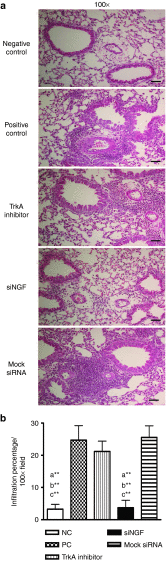
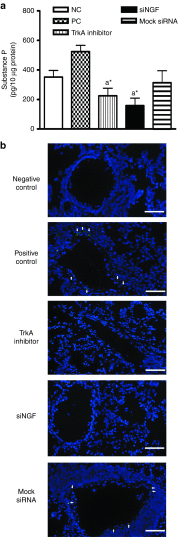
Airway hyperresponsiveness is the hallmark of allergic asthma and caused by multiple factors. Nerve growth factor (NGF), a neurotrophin, is originally known for regulation of neural circuit development and function. Recent studies indicated that NGF contributes to airway hyperresponsiveness and pathogenesis of asthma. The objective of this study is to develop a small interfering RNA against NGF to attenuate airway hyperresponsiveness and further elucidate the underlying mechanism. In a murine model of allergic asthma, the ovalbumin-sensitized mice were intratracheally delivered small interfering RNA against NGF or administered an inhibitor targeting NGF receptor, tropomyosin-related kinase A, as a positive treatment control. In this study, knockdown NGF derived from pulmonary epithelium significantly reduced airway resistance in vivo. The levels of NGF, proinflammatory cytokines and infiltrated eosinophils in airway were decreased in small interfering RNA against NGF group but not in tropomyosin-related kinase A inhibitor and mock siRNA group. Furthermore, induction of neuropeptide (substance P) and airway innervation were mediated by NGF/tropomyosin-related kinase A pathway. These findings suggested that NGF targeting treatment holds the potential therapy for antigen-induced airway hyperresponsiveness via attenuation of airway innervation and inflammation in asthma.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Nerve growth factor derived from bronchial epithelium after chronic mite antigen exposure contributes to airway hyperresponsiveness by inducing hyperinnervation, and is inhibited by in vivo siRNA.Clin Exp Allergy. 2012 Mar;42(3):460-70. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.2011.03918.x. Epub 2011 Dec 14. Clin Exp Allergy. 2012. PMID: 22168511
-
Airway hyper-responsiveness in allergic asthma in guinea-pigs is mediated by nerve growth factor via the induction of substance P: a potential role for trkA.Clin Exp Allergy. 2006 Sep;36(9):1192-200. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.2006.02549.x. Clin Exp Allergy. 2006. PMID: 16961720
-
Airway epithelial cells produce neurotrophins and promote the survival of eosinophils during allergic airway inflammation.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2006 Apr;117(4):787-94. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2005.12.1339. Epub 2006 Feb 21. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2006. PMID: 16630935
-
Airway hyperresponsiveness: first eosinophils and then neuropeptides.Int J Immunopharmacol. 1997 Sep-Oct;19(9-10):517-27. doi: 10.1016/s0192-0561(97)00085-4. Int J Immunopharmacol. 1997. PMID: 9637348 Review.
-
Nerve growth factor and its receptors in asthma and inflammation.Eur J Pharmacol. 2004 Oct 1;500(1-3):453-65. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2004.07.044. Eur J Pharmacol. 2004. PMID: 15464052 Review.
Cited by
-
Pulmonary Delivery of siRNA via Polymeric Vectors as Therapies of Asthma.Arch Pharm (Weinheim). 2015 Oct;348(10):681-8. doi: 10.1002/ardp.201500120. Epub 2015 Jul 7. Arch Pharm (Weinheim). 2015. PMID: 26148454 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanisms of organophosphorus pesticide toxicity in the context of airway hyperreactivity and asthma.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2018 Oct 1;315(4):L485-L501. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00211.2018. Epub 2018 Jun 28. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2018. PMID: 29952220 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neurotrophins in Asthma.Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 2018 Feb 16;18(2):10. doi: 10.1007/s11882-018-0765-y. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 2018. PMID: 29453651 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting TSLP With shRNA Alleviates Airway Inflammation and Decreases Epithelial CCL17 in a Murine Model of Asthma.Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2016 May 3;5(5):e316. doi: 10.1038/mtna.2016.29. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2016. PMID: 27138176 Free PMC article.
-
BIGKnock: fine-mapping gene-based associations via knockoff analysis of biobank-scale data.Genome Biol. 2023 Feb 13;24(1):24. doi: 10.1186/s13059-023-02864-6. Genome Biol. 2023. PMID: 36782330 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hargreave FE, Dolovich J, O'Byrne PM, Ramsdale EH, Daniel EE. The origin of airway hyperresponsiveness. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1986;78 5 Pt 1:825–832. - PubMed
-
- Baroffio M, Barisione G, Crimi E, Brusasco V. Noninflammatory mechanisms of airway hyper-responsiveness in bronchial asthma: an overview. Ther Adv Respir Dis. 2009;3:163–174. - PubMed
-
- Lykissas MG, Batistatou AK, Charalabopoulos KA, Beris AE. The role of neurotrophins in axonal growth, guidance, and regeneration. Curr Neurovasc Res. 2007;4:143–151. - PubMed
-
- Donnerer J, Schuligoi R, Stein C. Increased content and transport of substance P and calcitonin gene-related peptide in sensory nerves innervating inflamed tissue: evidence for a regulatory function of nerve growth factor in vivo. Neuroscience. 1992;49:693–698. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

