Tissue-resident natural killer (NK) cells are cell lineages distinct from thymic and conventional splenic NK cells
- PMID: 24714492
- PMCID: PMC3975579
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.01659
Tissue-resident natural killer (NK) cells are cell lineages distinct from thymic and conventional splenic NK cells
Abstract
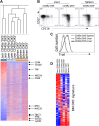
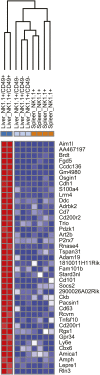
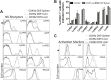
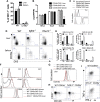
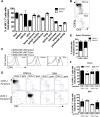
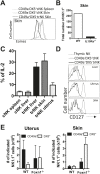
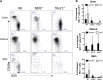
Natural killer (NK) cells belong to the innate immune system; they can control virus infections and developing tumors by cytotoxicity and producing inflammatory cytokines. Most studies of mouse NK cells, however, have focused on conventional NK (cNK) cells in the spleen. Recently, we described two populations of liver NK cells, tissue-resident NK (trNK) cells and those resembling splenic cNK cells. However, their lineage relationship was unclear; trNK cells could be developing cNK cells, related to thymic NK cells, or a lineage distinct from both cNK and thymic NK cells. Herein we used detailed transcriptomic, flow cytometric, and functional analysis and transcription factor-deficient mice to determine that liver trNK cells form a distinct lineage from cNK and thymic NK cells. Taken together with analysis of trNK cells in other tissues, there are at least four distinct lineages of NK cells: cNK, thymic, liver (and skin) trNK, and uterine trNK cells. DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.7554/eLife.01659.001.
Keywords: liver; skin; uterus.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that no competing interests exist.
Figures



References
-
- Ashkar AA, Black GP, Wei Q, He H, Liang L, Head JR, Croy BA. 2003. Assessment of requirements for IL-15 and IFN regulatory factors in uterine NK cell differentiation and function during pregnancy. Journal of Immunology 171:2937–2944 - PubMed
-
- Ashkar AA, Di Santo JP, Croy BA. 2000. Interferon gamma contributes to initiation of uterine vascular modification, decidual integrity, and uterine natural killer cell maturation during normal murine pregnancy. The Journal of Experimental Medicine 192:259–270. 10.1084/jem.192.2.259 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Barber EM, Pollard JW. 2003. The uterine NK cell population requires IL-15 but these cells are not required for pregnancy nor the resolution of a Listeria monocytogenes infection. Journal of Immunology 171:37–46 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

