In vivo reprogramming of pancreatic acinar cells to three islet endocrine subtypes
- PMID: 24714494
- PMCID: PMC3977343
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.01846
In vivo reprogramming of pancreatic acinar cells to three islet endocrine subtypes
Abstract
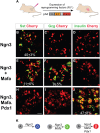
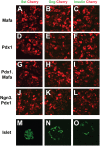
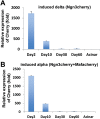
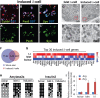
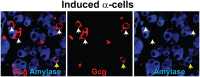
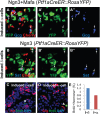
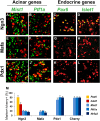
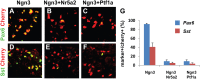
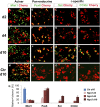
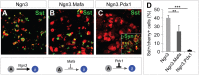
Direct lineage conversion of adult cells is a promising approach for regenerative medicine. A major challenge of lineage conversion is to generate specific cell subtypes. The pancreatic islets contain three major hormone-secreting endocrine subtypes: insulin(+) β-cells, glucagon(+) α-cells, and somatostatin(+) δ-cells. We previously reported that a combination of three transcription factors, Ngn3, Mafa, and Pdx1, directly reprograms pancreatic acinar cells to β-cells. We now show that acinar cells can be converted to δ-like and α-like cells by Ngn3 and Ngn3+Mafa respectively. Thus, three major islet endocrine subtypes can be derived by acinar reprogramming. Ngn3 promotes establishment of a generic endocrine state in acinar cells, and also promotes δ-specification in the absence of other factors. δ-specification is in turn suppressed by Mafa and Pdx1 during α- and β-cell induction. These studies identify a set of defined factors whose combinatorial actions reprogram acinar cells to distinct islet endocrine subtypes in vivo. DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.7554/eLife.01846.001.
Keywords: acinar to endocrine conversion; direct lineage conversion; in vivo reprogramming; islet delta, alpha, beta cells; pancreatic endocrine cells.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that no competing interests exist.
Figures


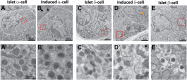

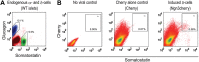


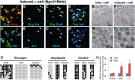

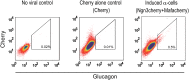



References
-
- Beres TM, Masui T, Swift GH, Shi L, Henke RM, MacDonald RJ. 2006. PTF1 is an organ-specific and Notch-independent basic helix-loop-helix complex containing the mammalian Suppressor of Hairless (RBP-J) or its paralogue, RBP-L. Molecular and Cellular Biology 26:117–130 doi: 10.1128/MCB.26.1.117-130.2006 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Caiazzo M, Dell’Anno MT, Dvoretskova E, Lazarevic D, Taverna S, Leo D, Sotnikova TD, Menegon A, Roncaglia P, Colciago G, Russo G, Carninci P, Pezzoli G, Gainetdinov RR, Gustincich S, Dityatev A, Broccoli V. 2011. Direct generation of functional dopaminergic neurons from mouse and human fibroblasts. Nature 476:224–227 doi: 10.1038/nature10284 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

