Vitamin D intake, blood 25(OH)D levels, and breast cancer risk or mortality: a meta-analysis
- PMID: 24714744
- PMCID: PMC4037823
- DOI: 10.1038/bjc.2014.175
Vitamin D intake, blood 25(OH)D levels, and breast cancer risk or mortality: a meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Experimental studies suggest potential anti-carcinogenic properties of vitamin D against breast cancer risk, but the epidemiological evidence to date is inconsistent.
Methods: We searched MEDLINE and EMBASE databases along with a hand search for eligible studies to examine the association between vitamin D status (based on diet and blood 25-hydroxyvitamin D (25(OH)D)) and breast cancer risk or mortality in a meta-analysis. A random-effect model was used to calculate a pooled adjusted relative risk (RR).
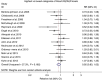
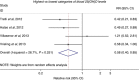
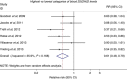
Results: A total of 30 prospective studies (nested case-control or cohort) were included for breast cancer incidence (n=24 studies; 31 867 cases) or mortality (n=6 studies; 870 deaths) among 6092 breast cancer patients. The pooled RRs of breast cancer incidence for the highest vs the lowest vitamin D intake and blood 25(OH)D levels were 0.95 (95% CI: 0.88-1.01) and 0.92 (95% CI: 0.83-1.02), respectively. Among breast cancer patients, high blood 25(OH)D levels were significantly associated with lower breast cancer mortality (pooled RR=0.58, 95% CI: 0.40-0.85) and overall mortality (pooled RR=0.61, 95% CI: 0.48-0.79). There was no evidence of heterogeneity and publication bias.
Conclusions: Our findings suggest that high vitamin D status is weakly associated with low breast cancer risk but strongly associated with better breast cancer survival.
Figures

References
-
- Abbas S, Linseisen J, Rohrmann S, Chang-Claude J, Peeters PH, Engel P, Brustad M, Lund E, Skeie G, Olsen A, Tjonneland A, Overvad K, Boutron-Ruault MC, Clavel-Chapelon F, Fagherazzi G, Kaaks R, Boeing H, Buijsse B, Adarakis G, Ouranos V, Trichopoulou A, Masala G, Krogh V, Mattiello A, Tumino R, Sacerdote C, Buckland G, Suarez MV, Sanchez MJ, Chirlaque MD, Barricarte A, Amiano P, Manjer J, Wirfalt E, Lenner P, Sund M, Bueno-de-Mesquita HB, van Duijnhoven FJ, Khaw KT, Wareham N, Key TJ, Fedirko V, Romieu I, Gallo V, Norat T, Wark PA, Riboli E. Dietary intake of vitamin d and calcium and breast cancer risk in the European prospective investigation into cancer and nutrition. Nutr Cancer. 2013;65 (2:178–187. - PubMed
-
- Agborsangaya CB, Surcel HM, Toriola AT, Pukkala E, Parkkila S, Tuohimaa P, Lukanova A, Lehtinen M. Serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D at pregnancy and risk of breast cancer in a prospective study. Eur J Cancer. 2010;46 (3:467–470. - PubMed
-
- Almquist M, Bondeson AG, Bondeson L, Malm J, Manjer J. Serum levels of vitamin D, PTH and calcium and breast cancer risk—a prospective nested case-control study. Int J Cancer. 2010;127 (9:2159–2168. - PubMed
-
- Anderson LN, Cotterchio M, Kirsh VA, Knight JA. Ultraviolet sunlight exposure during adolescence and adulthood and breast cancer risk: a population-based case-control study among Ontario women. Am J Epidemiol. 2011;174 (3:293–304. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

