Gene silencing of NOB1 by lentivirus suppresses growth and migration of human osteosarcoma cells
- PMID: 24714960
- PMCID: PMC4055445
- DOI: 10.3892/mmr.2014.2119
Gene silencing of NOB1 by lentivirus suppresses growth and migration of human osteosarcoma cells
Erratum in
-
[Corrigendum] Gene silencing of NOB1 by lentivirus suppresses growth and migration of human osteosarcoma cells.Mol Med Rep. 2023 Feb;27(2):22. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2022.12909. Epub 2022 Dec 9. Mol Med Rep. 2023. PMID: 36484386 Free PMC article.
Abstract
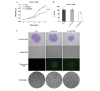
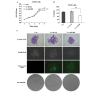
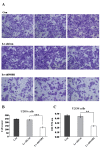
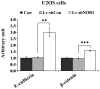
NIN1/RPN12 binding protein 1 homolog (Saccharomyces cerevisiae) (NOB1) encodes a chaperone protein that joins the 20S proteasome with the 19S regulatory particle in the nucleus and facilitates the biogenesis of the 26S proteasome, which plays a role in maintaining cellular homeostasis by controlling protein degradation. In order to investigate the role of NOB1 in osteosarcoma, NOB1 protein expression in human osteosarcoma cell lines was assessed using western blot analysis. Lentivirus-mediated short hairpin RNA was employed to knock down NOB1, and the effects of NOB1 silencing on cell growth were assessed using MTT, colony formation and cell cycle assays. Cell migration was observed using the Transwell assay. In addition, the expression levels of E-cadherin and β-catenin were examined by western blot analysis. Functional analysis indicated that NOB1-knockdown markedly inhibited cell growth and caused G2/M-phase arrest in human osteosarcoma cells. Furthermore, NOB1 inhibition decreased cell migration and increased E-cadherin and β-catenin expression in U2OS cells. In conclusion, the present study suggested that NOB1 depletion may inhibit osteosarcoma development by increasing E-cadherin and β-catenin expression and, for the first time, indicated the potential of NOB1 as a target in osteosarcoma treatment.
Figures


References
-
- Glickman MH, Ciechanover A. The ubiquitin-proteasome proteolytic pathway: destruction for the sake of construction. Physiol Rev. 2002;82:373–428. - PubMed
-
- Ferrell K, Wilkinson CR, Dubiel W, Gordon C. Regulatory subunit interactions of the 26S proteasome, a complex problem. Trends Biochem Sci. 2000;25:83–88. - PubMed
-
- Frezza M, Schmit S, Dou QP. Targeting the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway: an emerging concept in cancer therapy. Curr Top Med Chem. 2011;11:2888–2905. - PubMed
-
- Yerlikaya A, Yöntem M. The significance of ubiquitin proteasome pathway in cancer development. Recent Pat Anticancer Drug Discov. 2013;8:298–309. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

