Recommended implementation of arterial spin-labeled perfusion MRI for clinical applications: A consensus of the ISMRM perfusion study group and the European consortium for ASL in dementia
- PMID: 24715426
- PMCID: PMC4190138
- DOI: 10.1002/mrm.25197
Recommended implementation of arterial spin-labeled perfusion MRI for clinical applications: A consensus of the ISMRM perfusion study group and the European consortium for ASL in dementia
Abstract
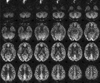
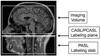
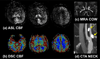
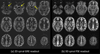
This review provides a summary statement of recommended implementations of arterial spin labeling (ASL) for clinical applications. It is a consensus of the ISMRM Perfusion Study Group and the European ASL in Dementia consortium, both of whom met to reach this consensus in October 2012 in Amsterdam. Although ASL continues to undergo rapid technical development, we believe that current ASL methods are robust and ready to provide useful clinical information, and that a consensus statement on recommended implementations will help the clinical community to adopt a standardized approach. In this review, we describe the major considerations and trade-offs in implementing an ASL protocol and provide specific recommendations for a standard approach. Our conclusion is that as an optimal default implementation, we recommend pseudo-continuous labeling, background suppression, a segmented three-dimensional readout without vascular crushing gradients, and calculation and presentation of both label/control difference images and cerebral blood flow in absolute units using a simplified model.
Keywords: arterial spin labeling; cerebral blood flow; perfusion.
© 2014 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures

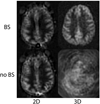
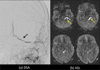
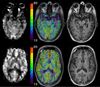
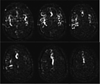
References
-
- Bokkers RP, Bremmer JP, van Berckel BN, Lammertsma AA, Hendrikse J, Pluim JP, Kappelle LJ, Boellaard R, Klijn CJ. Arterial spin labeling perfusion MRI at multiple delay times: a correlative study with H(2)(15)O positron emission tomography in patients with symptomatic carotid artery occlusion. Journal of cerebral blood flow and metabolism : official journal of the International Society of Cerebral Blood Flow and Metabolism. 2010;30(1):222–229. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Xu G, Rowley HA, Wu G, Alsop DC, Shankaranarayanan A, Dowling M, Christian BT, Oakes TR, Johnson SC. Reliability and precision of pseudo-continuous arterial spin labeling perfusion MRI on 3.0 T and comparison with 15O-water PET in elderly subjects at risk for Alzheimer's disease. NMR in biomedicine. 2010;23(3):286–293. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Gevers S, van Osch MJ, Bokkers RP, Kies DA, Teeuwisse WM, Majoie CB, Hendrikse J, Nederveen AJ. Intra- and multicenter reproducibility of pulsed, continuous and pseudo-continuous arterial spin labeling methods for measuring cerebral perfusion. Journal of cerebral blood flow and metabolism : official journal of the International Society of Cerebral Blood Flow and Metabolism. 2011;31(8):1706–1715. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

