The roles of reactive oxygen metabolism in drought: not so cut and dried
- PMID: 24715539
- PMCID: PMC3982730
- DOI: 10.1104/pp.113.233478
The roles of reactive oxygen metabolism in drought: not so cut and dried
Abstract
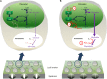
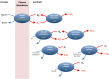
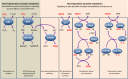
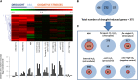
Drought is considered to cause oxidative stress, but the roles of oxidant-induced modifications in plant responses to water deficit remain obscure. Key unknowns are the roles of reactive oxygen species (ROS) produced at specific intracellular or apoplastic sites and the interactions between the complex, networking antioxidative systems in restricting ROS accumulation or in redox signal transmission. This Update discusses the physiological aspects of ROS production during drought, and analyzes the relationship between oxidative stress and drought from different but complementary perspectives. We ask to what extent redox changes are involved in plant drought responses and discuss the roles that different ROS-generating processes may play. Our discussion emphasizes the complexity and the specificity of antioxidant systems, and the likely importance of thiol systems in drought-induced redox signaling. We identify candidate drought-responsive redox-associated genes and analyze the potential importance of different metabolic pathways in drought-associated oxidative stress signaling.
Figures

References
-
- Achard P, Renou JP, Berthomé R, Harberd NP, Genschik P. (2008) Plant DELLAs restrain growth and promote survival of adversity by reducing the levels of reactive oxygen species. Curr Biol 18: 656–660 - PubMed
-
- Angelini R, Cona A, Federico R, Fincato P, Tavladoraki P, Tisi A. (2010) Plant amine oxidases “on the move”: an update. Plant Physiol Biochem 48: 560–564 - PubMed
-
- Bartoli CG, Guaimet JJ, Kiddle G, Pastori GM, Di Cagno R, Theodoulou F, Foyer CH. (2005) Ascorbate content of wheat leaves is not determined by maximal l-galactono-1,4-lactone dehydrogenase (GalLDH) activity under drought stress. Plant Cell Environ 28: 1073–1081
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

