Chemical Constituents and Pharmacology of the Aristolochia ( mădōu ling) species
- PMID: 24716140
- PMCID: PMC3942903
- DOI: 10.1016/s2225-4110(16)30111-0
Chemical Constituents and Pharmacology of the Aristolochia ( mădōu ling) species
Abstract
Aristolochia ( mădōu ling) is an important genus widely cultivated and had long been known for their extensive use in traditional Chinese medicine. The genus has attracted so much great interest because of their numerous biological activity reports and unique constituents, aristolochic acids (AAs). In 2004, we reviewed the metabolites of Aristolochia species which have appeared in the literature, concerning the isolation, structural elucidation, biological activity and literature references. In addition, the nephrotoxicity of aristolochic acids, biosynthetic studies, ecological adaptation, and chemotaxonomy researches were also covered in the past review. In the present manuscript, we wish to review the various physiologically active compounds of different classes reported from Aristolochia species in the period between 2004 and 2011. In regard to the chemical and biological aspects of the constituents from the Aristolochia genus, this review would address the continuous development in the phytochemistry and the therapeutic application of the Aristolochia species. Moreover, the recent nephrotoxicity studies related to aristolochic acids would be covered in this review and the structure-toxicity relationship would be discussed.
Keywords: Alkaloid; Aristolochia; Aristolochic acid; Bioactivity; Flavonoid; Terpenoid.
Figures
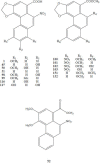
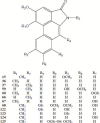

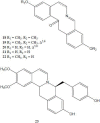
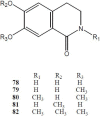


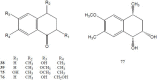
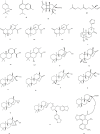
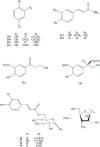
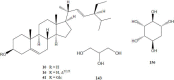
References
-
- Alviano W.S, Alviano D.S, Diniz C.G, Antoniolli A.R, Alviano C.S, Farias L.M, Carvalho M.A.R, Souza M.M.G, Bolognese A.M. In vitro antioxidant potential of medicinal plant extracts and their activities against oral bacteria based on Brazilian folk medicine. Archives of Oral Biology. 2008;53:545–552. - PubMed
-
- Andrei Ed. Sao Paulo: 1977. Farmacopeia homeopatica Brasileira.
-
- Balachandran P, Wei F, Lin R.C, Khan I.A, Pasco D.S. Structure activity relationships of aristolochic acid analogues: toxicity in cultured renal epithelial cells. Kidney International. 2005;67:1797–1805. - PubMed
-
- Balbach A. 11th Ed. Sao Paulo: Edel; 1979. Flora nacional na medicina domestica; p. 45. 458, 573, 739, 840.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
