Continuous venovenous hemofiltration versus extended daily hemofiltration in patients with septic acute kidney injury: a retrospective cohort study
- PMID: 24716613
- PMCID: PMC4056629
- DOI: 10.1186/cc13827
Continuous venovenous hemofiltration versus extended daily hemofiltration in patients with septic acute kidney injury: a retrospective cohort study
Abstract
Introduction: Whether continuous venovenous hemofiltration (CVVHF) is superior to extended daily hemofiltration (EDHF) for the treatment of septic AKI is unknown. We compared the effect of CVVHF (greater than 72 hours) with EDHF (8 to 12 hours daily) on renal recovery and mortality in patients with severe sepsis or septic shock and concurrent acute kidney injury (AKI).
Methods: A retrospective analysis of 145 septic AKI patients who underwent renal replacement therapy (RRT) between July 2009 and May 2013 was performed. These patients were treated by CVVHF or EDHF with the same polyacrylonitrile membrane and bicarbonate-based buffer. The primary outcomes measured were occurrence of renal recovery and all-cause mortality by 60 days.
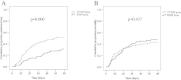
Results: Sixty-five and eighty patients were treated with CVVHF and EDHF, respectively. Patients in the CVVHF group had significantly higher recovery of renal function (50.77% of CVVHF group versus 32.50% in the EDHF group, P = 0.026). Median time to renal recovery was 17.26 days for CVVHF patients and 25.46 days for EDHF patients (P = 0.039). Sixty-day all-cause mortality was similar between CVVHF and EDHF groups (44.62%, and 46.25%, respectively; P = 0.844). 55.38% of patients on CVVHF and 28.75% on EDHF developed hypophosphatemia (P = 0.001). The other adverse events related to RRT did not differ between groups. On multivariate analysis, including physiologically clinical relevant variables, CVVHF therapy was significantly associated with recovery of renal function (HR 3.74; 95% CI 1.82 to 7.68; P < 0.001), but not with mortality (HR 0.69; 95% CI 0.34 to 1.41; P = 0.312).
Conclusions: Patients undergoing CVVHF therapy had significantly improved renal recovery independent of clinically relevant variables. The patients with septic AKI had similar 60-day all-cause mortality rates, regardless of type of RRT.
Figures
Comment in
-
Renal recovery after acute kidney injury: choice of initial renal replacement therapy modality still matters.Crit Care. 2014 Jun 20;18(3):154. doi: 10.1186/cc13936. Crit Care. 2014. PMID: 25042793 Free PMC article.
Similar articles
-
Vancomycin clearance during continuous venovenous haemofiltration in critically ill patients.Intensive Care Med. 1999 Oct;25(10):1100-4. doi: 10.1007/s001340051018. Intensive Care Med. 1999. PMID: 10551965 Clinical Trial.
-
Plasma concentrations and clearance of procalcitonin during continuous veno-venous hemofiltration in septic patients.Shock. 2001 Mar;15(3):171-5. doi: 10.1097/00024382-200115030-00002. Shock. 2001. PMID: 11236898
-
Continuous veno-venous hemofiltration improves hemodynamics in septic shock with acute renal failure without modifying TNFalpha and IL6 plasma concentrations.J Nephrol. 2002 Mar-Apr;15(2):150-7. J Nephrol. 2002. PMID: 12018631
-
The big bang of hemofiltration: the beginning of a new era in the third millennium for extra-corporeal blood purification!Int J Artif Organs. 2006 Jul;29(7):649-59. doi: 10.1177/039139880602900702. Int J Artif Organs. 2006. PMID: 16874669 Review.
-
Blood Purification Techniques for Sepsis and Septic AKI.Semin Nephrol. 2019 Sep;39(5):505-514. doi: 10.1016/j.semnephrol.2019.06.010. Semin Nephrol. 2019. PMID: 31514914 Review.
Cited by
-
Renal Function Outcome Prognosis in Septic and Non-septic Acute Kidney Injury Patients.Med Arch. 2015 Apr;69(2):77-80. doi: 10.5455/medarh.2015.69.77-80. Epub 2015 Apr 6. Med Arch. 2015. PMID: 26005252 Free PMC article.
-
Biomarkers of renal recovery after acute kidney injury.Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2017 Jul-Sep;29(3):373-381. doi: 10.5935/0103-507X.20170051. Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2017. PMID: 29044306 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clinical approach to the patient with AKI and sepsis.Semin Nephrol. 2015 Jan;35(1):12-22. doi: 10.1016/j.semnephrol.2015.01.003. Semin Nephrol. 2015. PMID: 25795496 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Simplified regional citrate anticoagulation protocol for CVVH, CVVHDF and SLED focused on the prevention of KRT-related hypophosphatemia while optimizing acid-base balance.Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2023 Sep 29;38(10):2298-2309. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfad068. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2023. PMID: 37037771 Free PMC article.
-
[Acute kidney injury : A clinical syndrome].Internist (Berl). 2016 Oct;57(10):983-993. doi: 10.1007/s00108-016-0138-3. Internist (Berl). 2016. PMID: 27654909 Review. German.
References
-
- Buchardi H. History and development of continuous renal replacement techniques. Kidney Int Suppl. 1998;66:S120–S124. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

