The HIV-1 Tat protein modulates CD4 expression in human T cells through the induction of miR-222
- PMID: 24717285
- PMCID: PMC4075518
- DOI: 10.4161/rna.28372
The HIV-1 Tat protein modulates CD4 expression in human T cells through the induction of miR-222
Abstract
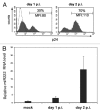
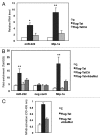
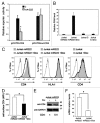
Several cellular microRNAs show substantial changes in expression during HIV-1 infection and their active role in the viral life cycle is progressively emerging. In the present study, we found that HIV-1 infection of Jurkat T cells significantly induces the expression of miR-222. We show that this induction depends on HIV-1 Tat protein, which is able to increase the transcriptional activity of NFkB on miR-222 promoter. Moreover, we demonstrate that miR-222 directly targets CD4, a key receptor for HIV-1, thus reducing its expression. We propose that Tat, by inducing miR-222 expression, complements the CD4 downregulation activity exerted by other viral proteins (i.e., Nef, Vpu, and Env), and we suggest that this represents a novel mechanism through which HIV-1 efficiently represses CD4 expression in infected cells.
Keywords: CD4; HIV-1; NFkB; microRNAs; post-transcriptional regulation.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
