Effects of neuropeptides and mechanical loading on bone cell resorption in vitro
- PMID: 24717410
- PMCID: PMC4013601
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms15045874
Effects of neuropeptides and mechanical loading on bone cell resorption in vitro
Abstract
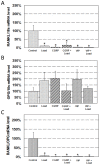
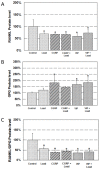
Neuropeptides such as vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP) and calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) are present in nerve fibers of bone tissues and have been suggested to potentially regulate bone remodeling. Oscillatory fluid flow (OFF)-induced shear stress is a potent signal in mechanotransduction that is capable of regulating both anabolic and catabolic bone remodeling. However, the interaction between neuropeptides and mechanical induction in bone remodeling is poorly understood. In this study, we attempted to quantify the effects of combined neuropeptides and mechanical stimuli on mRNA and protein expression related to bone resorption. Neuropeptides (VIP or CGRP) and/or OFF-induced shear stress were applied to MC3T3-E1 pre-osteoblastic cells and changes in receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) ligand (RANKL) and osteoprotegerin (OPG) mRNA and protein levels were quantified. Neuropeptides and OFF-induced shear stress similarly decreased RANKL and increased OPG levels compared to control. Changes were not further enhanced with combined neuropeptides and OFF-induced shear stress. These results suggest that neuropeptides CGRP and VIP have an important role in suppressing bone resorptive activities through RANKL/OPG pathway, similar to mechanical loading.
Figures

Similar articles
-
[Inhibitory effect of diacerein on osteoclastic bone destruction and its possible mechanism of action].Yao Xue Xue Bao. 2006 Jun;41(6):555-60. Yao Xue Xue Bao. 2006. PMID: 16927832 Chinese.
-
Effects of high frequency loading on RANKL and OPG mRNA expression in ST-2 murine stromal cells.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2009 Sep 4;10:109. doi: 10.1186/1471-2474-10-109. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2009. PMID: 19728893 Free PMC article.
-
Oscillatory fluid flow-induced shear stress decreases osteoclastogenesis through RANKL and OPG signaling.Bone. 2006 Nov;39(5):1043-1047. doi: 10.1016/j.bone.2006.05.017. Epub 2006 Jul 24. Bone. 2006. PMID: 16860618
-
Receptor activator of nuclear factor-κB ligand (RANKL)/RANK/osteoprotegerin system in bone and other tissues (review).Mol Med Rep. 2015 May;11(5):3212-8. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2015.3152. Epub 2015 Jan 7. Mol Med Rep. 2015. PMID: 25572286 Review.
-
[Animal models for bone and joint disease. Bone disease of osteoprotegerin deficient mouse].Clin Calcium. 2011 Feb;21(2):190-6. Clin Calcium. 2011. PMID: 21289415 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
Optogenetic activation of mechanical nociceptions to enhance implant osseointegration.Nat Commun. 2025 Mar 31;16(1):3093. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-58336-x. Nat Commun. 2025. PMID: 40164597 Free PMC article.
-
Peripheral Nerve Fibers and Their Neurotransmitters in Osteoarthritis Pathology.Int J Mol Sci. 2017 Apr 28;18(5):931. doi: 10.3390/ijms18050931. Int J Mol Sci. 2017. PMID: 28452955 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Research Progress in Calcitonin Gene-Related Peptide and Bone Repair.Biomolecules. 2023 May 15;13(5):838. doi: 10.3390/biom13050838. Biomolecules. 2023. PMID: 37238709 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Neuropeptide HGAP Regulates Growth, Reproduction, Metamorphosis, Tissue Damage Repair, and Response against Starvation in Pacific Abalone.Neuroendocrinology. 2024;114(5):453-467. doi: 10.1159/000535945. Epub 2023 Dec 23. Neuroendocrinology. 2024. PMID: 38142675 Free PMC article.
-
Feasibility of administration of calcitonin gene-related peptide receptor antagonist on attenuation of pain and progression in osteoarthritis.Sci Rep. 2023 Sep 16;13(1):15354. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-42673-2. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37717108 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Reddi A.H. Bone morphogenesis and modeling: Soluble signals sculpt osteosomes in the solid state. Cell. 1997;89:159–161. - PubMed
-
- Rodan G.A., Martin T.J. Role of osteoblasts in hormonal control of bone resorption—A hypothesis. Calcif. Tissue Int. 1981;33:349–351. - PubMed
-
- Matsuo K., Irie N. Osteoclast-osteoblast communication. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2008;473:201–209. - PubMed
-
- Lacey D.L., Timms E., Tan H.L., Kelley M.J., Dunstan C.R., Burgess T., Elliott R., Colombero A., Elliott G., Scully S., et al. Osteoprotegerin ligand is a cytokine that regulates osteoclast differentiation and activation. Cell. 1998;93:165–176. - PubMed
-
- Secchiero P., Vaccarezza M., Gonelli A., Zauli G. TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL): A potential candidate for combined treatment of hematological malignancies. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2004;10:3673–3681. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

