Epigenetic regulation of the placental HSD11B2 barrier and its role as a critical regulator of fetal development
- PMID: 24717516
- PMCID: PMC4065178
- DOI: 10.4161/epi.28703
Epigenetic regulation of the placental HSD11B2 barrier and its role as a critical regulator of fetal development
Abstract
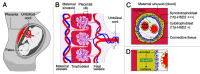
"Fetal programming" is a term used to describe how early-life experience influences fetal development and later disease risk. In humans, prenatal stress-induced fetal programming is associated with increased risk of preterm birth, and a heightened risk of metabolic and neurological diseases later in life. A critical determinant of this is the regulation of fetal exposure to glucocorticoids by the placenta. Glucocorticoids are the mediators through which maternal stress influences fetal development. Excessive fetal glucocorticoid exposure during pregnancy results in low birth weight and abnormalities in a number of tissues. The amount of fetal exposure to maternal glucocorticoids depends on the expression of HSD11B2, an enzyme predominantly produced by the syncytiotrophoblast in the placenta. This protects the fetus by converting active glucocorticoids into inactive forms. In this review we examine recent findings regarding placental HSD11B2 that suggest that its epigenetic regulation may mechanistically link maternal stress and long-term health consequences in affected offspring.
Keywords: 11β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type-2; epigenetic; fetal outcome; placenta; prenatal stress.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Mechanisms for establishment of the placental glucocorticoid barrier, a guard for life.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2019 Jan;76(1):13-26. doi: 10.1007/s00018-018-2918-5. Epub 2018 Sep 17. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2019. PMID: 30225585 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epigenetic effects of prenatal stress on 11β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase-2 in the placenta and fetal brain.PLoS One. 2012;7(6):e39791. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0039791. Epub 2012 Jun 26. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22761903 Free PMC article.
-
Glucocorticoid excess and the developmental origins of disease: two decades of testing the hypothesis--2012 Curt Richter Award Winner.Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2013 Jan;38(1):1-11. doi: 10.1016/j.psyneuen.2012.08.012. Epub 2012 Sep 19. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2013. PMID: 22998948 Review.
-
Environmental influences on placental programming and offspring outcomes following maternal immune activation.Brain Behav Immun. 2020 Jan;83:44-55. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2019.08.192. Epub 2019 Sep 4. Brain Behav Immun. 2020. PMID: 31493445 Free PMC article.
-
Early life corticosteroid overexposure: Epigenetic and fetal origins of adult diseases.Int J Gynaecol Obstet. 2024 Jan;164(1):40-46. doi: 10.1002/ijgo.14914. Epub 2023 Jun 15. Int J Gynaecol Obstet. 2024. PMID: 37318113 Review.
Cited by
-
Prenatal and postnatal influences on behavioral development in a mouse model of preconceptional stress.Neurobiol Stress. 2024 Feb 3;29:100614. doi: 10.1016/j.ynstr.2024.100614. eCollection 2024 Mar. Neurobiol Stress. 2024. PMID: 38357099 Free PMC article.
-
Prenatal Hypoxia-Induced Adverse Reaction to Mild Stress is Associated with Depressive-Like Changes in the Glucocorticoid System of Rats.Neurochem Res. 2023 May;48(5):1455-1467. doi: 10.1007/s11064-022-03837-0. Epub 2022 Dec 10. Neurochem Res. 2023. PMID: 36495386
-
Programming of Vascular Dysfunction by Maternal Stress: Immune System Implications.Front Physiol. 2022 Mar 10;13:787617. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2022.787617. eCollection 2022. Front Physiol. 2022. PMID: 35360231 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanisms for establishment of the placental glucocorticoid barrier, a guard for life.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2019 Jan;76(1):13-26. doi: 10.1007/s00018-018-2918-5. Epub 2018 Sep 17. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2019. PMID: 30225585 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Early Life Stress and Epigenetics in Late-onset Alzheimer's Dementia: A Systematic Review.Curr Genomics. 2018 Nov;19(7):522-602. doi: 10.2174/1389202919666171229145156. Curr Genomics. 2018. PMID: 30386171 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
