Global control of tuberculosis: from extensively drug-resistant to untreatable tuberculosis
- PMID: 24717628
- PMCID: PMC5526327
- DOI: 10.1016/S2213-2600(14)70031-1
Global control of tuberculosis: from extensively drug-resistant to untreatable tuberculosis
Abstract
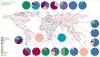
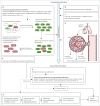
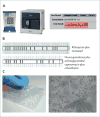
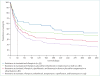
Extensively drug-resistant tuberculosis is a burgeoning global health crisis mainly affecting economically active young adults, and has high mortality irrespective of HIV status. In some countries such as South Africa, drug-resistant tuberculosis represents less than 3% of all cases but consumes more than a third of the total national budget for tuberculosis, which is unsustainable and threatens to destabilise national tuberculosis programmes. However, concern about drug-resistant tuberculosis has been eclipsed by that of totally and extremely drug-resistant tuberculosis--ie, resistance to all or nearly all conventional first-line and second-line antituberculosis drugs. In this Review, we discuss the epidemiology, pathogenesis, diagnosis, management, implications for health-care workers, and ethical and medicolegal aspects of extensively drug-resistant tuberculosis and other resistant strains. Finally, we discuss the emerging problem of functionally untreatable tuberculosis, and the issues and challenges that it poses to public health and clinical practice. The emergence and growth of highly resistant strains of tuberculosis make the development of new drugs and rapid diagnostics for tuberculosis--and increased funding to strengthen global control efforts, research, and advocacy--even more pressing.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
We declare that we have no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- WHO. Global Tuberculosis Report 2012. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2012.
-
- WHO. The new WHO report on anti-tuberculosis drug resistance—multidrug and extensively drug-resistant TB (M/XDR-TB): 2010 global report on surveillance and response. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2011.
-
- Udwadia ZF, Amale RA, Ajbani KK, Rodrigues C. Totally drug-resistant tuberculosis in India. Clin Infect Dis. 2012;54:579–81. - PubMed
-
- Velayati AA, Masjedi MR, Farnia P, et al. Emergence of new forms of totally drug-resistant tuberculosis bacilli: super extensively drug-resistant tuberculosis or totally drug-resistant strains in Iran. Chest. 2009;136:420–25. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

