Neuroprotective effect of aquaporin-4 deficiency in a mouse model of severe global cerebral ischemia produced by transient 4-vessel occlusion
- PMID: 24717641
- PMCID: PMC4306422
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neulet.2014.03.073
Neuroprotective effect of aquaporin-4 deficiency in a mouse model of severe global cerebral ischemia produced by transient 4-vessel occlusion
Abstract
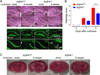
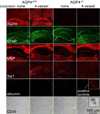
Astrocyte water channel aquaporin-4 (AQP4) facilitates water movement across the blood-brain barrier and into injured astrocytes. We previously showed reduced cytotoxic brain edema with improved neurological outcome in AQP4 knockout mice in water intoxication, infection and cerebral ischemia. Here, we established a 4-vessel transient occlusion model to test the hypothesis that AQP4 deficiency in mice could improve neurological outcome following severe global cerebral ischemia as occurs in cardiac arrest/resuscitation. Mice were subjected to 10-min transient bilateral carotid artery occlusion at 24h after bilateral vertebral artery cauterization. Cerebral blood flow was reduced during occlusion by >94% in both AQP4(+/+) and AQP4(-/-) mice. The primary outcome, neurological score, was remarkably better at 3 and 5 days after occlusion in AQP4(-/-) than in AQP4(+/+) mice, and survival was significantly improved as well. Brain water content was increased by 2.8±0.4% in occluded AQP4(+/+) mice, significantly greater than that of 0.3±0.6% in AQP4(-/-) mice. Histological examination and immunofluorescence of hippocampal sections at 5 days showed significantly greater neuronal loss in the CA1 region of hippocampus in AQP4(+/+) than AQP4(-/-) mice. The neuroprotection in mice conferred by AQP4 deletion following severe global cerebral ischemia provides proof-of-concept for therapeutic AQP4 inhibition to improve neurological outcome in cardiac arrest.
Keywords: AQP4; Astrocyte; Brain edema; Cerebral ischemia; Neuroprotection; Water transport.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Ireland Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Frigeri A, Gropper MA, Umenishi F, Kawashima M, Brown D, Verkman AS. Localization of MIWC and GLIP water channel homologs in neuromuscular, epithelial and glandular tissues. J. Cell Sci. 1995;108(Pt 9):2993–3002. - PubMed
-
- Manley GT, Fujimura M, Ma T, Noshita N, Filiz F, Bollen AW, Chan P, Verkman AS. Aquaporin-4 deletion in mice reduces brain edema after acute water intoxication and ischemic stroke. Nat. Med. 2000;6:159–163. - PubMed
-
- Papadopoulos MC, Verkman AS. Aquaporin-4 gene disruption in mice reduces brain swelling and mortality in pneumococcal meningitis. J. Biol. Chem. 2005;280:13906–13912. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

