Persistent salmonellosis causes pancreatitis in a murine model of infection
- PMID: 24717768
- PMCID: PMC3981665
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0092807
Persistent salmonellosis causes pancreatitis in a murine model of infection
Abstract
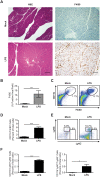
Pancreatitis, a known risk factor for the development of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma, is a serious, widespread medical condition usually caused by alcohol abuse or gallstone-mediated ductal obstruction. However, many cases of pancreatitis are of an unknown etiology. Pancreatitis has been linked to bacterial infection, but causality has yet to be established. Here, we found that persistent infection of mice with the bacterial pathogen Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium (S. Typhimurium) was sufficient to induce pancreatitis reminiscent of the human disease. Specifically, we found that pancreatitis induced by persistent S. Typhimurium infection was characterized by a loss of pancreatic acinar cells, acinar-to-ductal metaplasia, fibrosis and accumulation of inflammatory cells, including CD11b+ F4/80+, CD11b+ Ly6Cint Ly6G+ and CD11b+ Ly6Chi Ly6G- cells. Furthermore, we found that S. Typhimurium colonized and persisted in the pancreas, associated with pancreatic acinar cells in vivo, and could invade cultured pancreatic acinar cells in vitro. Thus, persistent infection of mice with S. Typhimurium may serve as a useful model for the study of pancreatitis as it relates to bacterial infection. Increased knowledge of how pathogenic bacteria can cause pancreatitis will provide a more integrated picture of the etiology of the disease and could lead to the development of new therapeutic approaches for treatment and prevention of pancreatitis and pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



References
-
- Whitcomb DC (2004) Inflammation and Cancer V. Chronic pancreatitis and pancreatic cancer. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 287: G315–319. - PubMed
-
- Fagenholz PJ, Castillo CF, Harris NS, Pelletier AJ, Camargo CA Jr (2007) Increasing United States hospital admissions for acute pancreatitis, 1988–2003. Ann Epidemiol 17: 491–497. - PubMed
-
- Tenner S, Sica G, Hughes M, Noordhoek E, Feng S, et al. (1997) Relationship of necrosis to organ failure in severe acute pancreatitis. Gastroenterology 113: 899–903. - PubMed
-
- Delrue LJ, De Waele JJ, Duyck PO (2010) Acute pancreatitis: radiologic scores in predicting severity and outcome. Abdom Imaging 35: 349–361. - PubMed
-
- Frey CF, Zhou H, Harvey DJ, White RH (2006) The incidence and case-fatality rates of acute biliary, alcoholic, and idiopathic pancreatitis in California, 1994–2001. Pancreas 33: 336–344. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

