Interleukin-19 impairment in active Crohn's disease patients
- PMID: 24718601
- PMCID: PMC3981722
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0093910
Interleukin-19 impairment in active Crohn's disease patients
Abstract
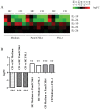
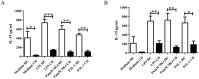
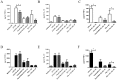
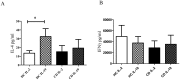
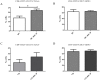
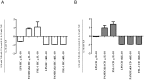
The exact function of interleukin-19 (IL-19) on immune response is poorly understood. In mice, IL-19 up-regulates TNFα and IL-6 expression and its deficiency increases susceptibility to DSS-induced colitis. In humans, IL-19 favors a Th2 response and is elevated in several diseases. We here investigate the expression and effects of IL-19 on cells from active Crohn's disease (CD) patient. Twenty-three active CD patients and 20 healthy controls (HC) were included. mRNA and protein IL-19 levels were analyzed in monocytes. IL-19 effects were determined in vitro on the T cell phenotype and in the production of cytokines by immune cells. We observed that unstimulated and TLR-activated monocytes expressed significantly lower IL-19 mRNA in active CD patients than in HC (logFC = -1.97 unstimulated; -1.88 with Pam3CSK4; and -1.91 with FSL-1; p<0.001). These results were confirmed at protein level. Exogenous IL-19 had an anti-inflammatory effect on HC but not on CD patients. IL-19 decreased TNFα production in PBMC (850.7 ± 75.29 pg/ml vs 2626.0 ± 350 pg/ml; p<0.01) and increased CTLA4 expression (22.04 ± 1.55% vs 13.98 ± 2.05%; p<0.05) and IL-4 production (32.5 ± 8.9 pg/ml vs 13.5 ± 2.9 pg/ml; p<0.05) in T cells from HC. IL-10 regulated IL-19 production in both active CD patients and HC. We observed that three of the miRNAs that can modulate IL-19 mRNA expression, were up-regulated in monocytes from active CD patients. These results suggested that IL-19 had an anti-inflammatory role in this study. Defects in IL-19 expression and the lack of response to this cytokine could contribute to inflammatory mechanisms in active CD patients.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Gallagher G, Dickensheets H, Eskdale J, Izotova LS, Mirochnitchenko OV, et al. (2000) Cloning, expression and initial characterization of interleukin-19 (IL-19), a novel homologue of human interleukin-10 (IL-10). Genes Immun 1: 442–450. - PubMed
-
- Dumoutier L, Leemans C, Lejeune D, Kotenko SV, Renauld JC (2001) Cutting edge: STAT activation by IL-19, IL-20 and mda-7 through IL-20 receptor complexes of two types. J Immunol 167: 3545–3549. - PubMed
-
- Oral HB, Kotenko SV, Yilmaz M, Mani O, Zumkehr J, et al. (2006) Regulation of T cells and cytokines by the interleukin-10 (IL-10)-family cytokines IL-19, IL-20, IL-22, IL-24 and IL-26. Eur J Immunol 36: 380–388. - PubMed
-
- Jordan WJ, Eskdale J, Boniotto M, Lennon GP, Peat J, et al. (2005) Human IL-19 regulates immunity through auto-induction of IL-19 and production of IL-10. Eur J Immunol 35: 1576–1582. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

