Nesprins: tissue-specific expression of epsilon and other short isoforms
- PMID: 24718612
- PMCID: PMC3981789
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0094380
Nesprins: tissue-specific expression of epsilon and other short isoforms
Abstract
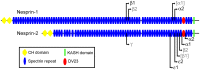
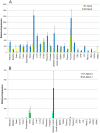
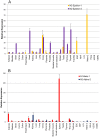
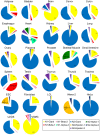
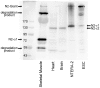
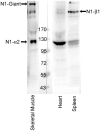
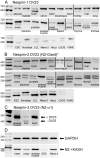
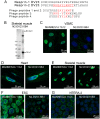
Nesprin-1-giant and nesprin-2-giant regulate nuclear positioning by the interaction of their C-terminal KASH domains with nuclear membrane SUN proteins and their N-terminal calponin-homology domains with cytoskeletal actin. A number of short isoforms lacking the actin-binding domains are produced by internal promotion. We have evaluated the significance of these shorter isoforms using quantitative RT-PCR and western blotting with site-specific monoclonal antibodies. Within a complete map of nesprin isoforms, we describe two novel nesprin-2 epsilon isoforms for the first time. Epsilon isoforms are similar in size and structure to nesprin-1-alpha. Expression of nesprin isoforms was highly tissue-dependent. Nesprin-2-epsilon-1 was found in early embryonic cells, while nesprin-2-epsilon-2 was present in heart and other adult tissues, but not skeletal muscle. Some cell lines lack shorter isoforms and express only one of the two nesprin genes, suggesting that either of the giant nesprins is sufficient for basic cell functions. For the first time, localisation of endogenous nesprin away from the nuclear membrane was shown in cells where removal of the KASH domain by alternative splicing occurs. By distinguishing between degradation products and true isoforms on western blots, it was found that previously-described beta and gamma isoforms are expressed either at only low levels or with a limited tissue distribution. Two of the shortest alpha isoforms, nesprin-1-alpha-2 and nesprin-2-alpha-1, were found almost exclusively in cardiac and skeletal muscle and a highly conserved and alternatively-spliced exon, available in both nesprin genes, was always included in these tissues. These "muscle-specific" isoforms are thought to form a complex with emerin and lamin A/C at the inner nuclear membrane and mutations in all three proteins cause Emery-Dreifuss muscular dystrophy and/or inherited dilated cardiomyopathy, disorders in which only skeletal muscle and/or heart are affected.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Apel ED, Lewis RM, Grady RM, Sanes JR (2000) Syne-1, a dystrophin- and klarsicht-related protein associated with synaptic nuclei at the neuromuscular junction. J Biol Chem 275: 31986–31995. - PubMed
-
- Zhang Q, Skepper JN, Yang F, Davies JD, Hegyi L, et al. (2001) Nesprins: a novel family of spectrin-repeat-containing proteins that localize to the nuclear membrane in multiple tissues. J Cell Sci 114: 4485–98. - PubMed
-
- Zhen YY, Libotte T, Munck M, Noegel AA, Korenbaum E (2002) NUANCE, a giant protein connecting the nucleus and actin cytoskeleton. J Cell Sci 115: 3207–3222. - PubMed
-
- Zhang Q, Ragnauth CD, Skepper JN, Worth NF, Warren DT, et al. (2005) Nesprin-2 is a multi-isomeric protein that binds lamin and emerin at the nuclear envelope and forms a subcellular network in skeletal muscle. J Cell Sci 118: 673–687. - PubMed
-
- Mislow JM, Kim MS, Davis DB, McNally EM (2002) Myne-1, a spectrin repeat transmembrane protein of the myocyte inner nuclear membrane, interacts with lamin A/C. J Cell Sci 115: 61–70. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

