Cholinergic modulation of large-conductance calcium-activated potassium channels regulates synaptic strength and spine calcium in cartwheel cells of the dorsal cochlear nucleus
- PMID: 24719104
- PMCID: PMC3983802
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3728-13.2014
Cholinergic modulation of large-conductance calcium-activated potassium channels regulates synaptic strength and spine calcium in cartwheel cells of the dorsal cochlear nucleus
Abstract
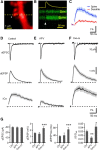
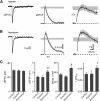
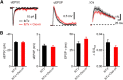
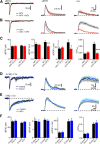
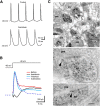
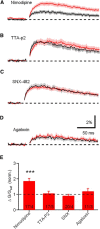
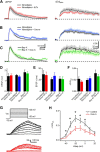
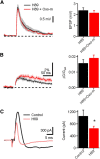
Acetylcholine is a neuromodulatory transmitter that controls synaptic plasticity and sensory processing in many brain regions. The dorsal cochlear nucleus (DCN) is an auditory brainstem nucleus that integrates auditory signals from the cochlea with multisensory inputs from several brainstem nuclei and receives prominent cholinergic projections. In the auditory periphery, cholinergic modulation serves a neuroprotective function, reducing cochlear output under high sound levels. However, the role of cholinergic signaling in the DCN is less understood. Here we examine postsynaptic mechanisms of cholinergic modulation at glutamatergic synapses formed by parallel fiber axons onto cartwheel cells (CWCs) in the apical DCN circuit from mouse brainstem slice using calcium (Ca) imaging combined with two-photon laser glutamate uncaging onto CWC spines. Activation of muscarinic acetylcholine receptors (mAChRs) significantly increased the amplitude of both uncaging-evoked EPSPs (uEPSPs) and spine Ca transients. Our results demonstrate that mAChRs in CWC spines act by suppressing large-conductance calcium-activated potassium (BK) channels, and this effect is mediated through the cAMP/protein kinase A signaling pathway. Blocking BK channels relieves voltage-dependent magnesium block of NMDA receptors, thereby enhancing uEPSPs and spine Ca transients. Finally, we demonstrate that mAChR activation inhibits L-type Ca channels and thus may contribute to the suppression of BK channels by mAChRs. In summary, we demonstrate a novel role for BK channels in regulating glutamatergic transmission and show that this mechanism is under modulatory control of mAChRs.
Figures
Similar articles
-
M1 muscarinic receptors boost synaptic potentials and calcium influx in dendritic spines by inhibiting postsynaptic SK channels.Neuron. 2010 Dec 9;68(5):936-47. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2010.09.004. Neuron. 2010. PMID: 21145006 Free PMC article.
-
Selective activation of BK channels in small-headed dendritic spines suppresses excitatory postsynaptic potentials.J Physiol. 2022 May;600(9):2165-2187. doi: 10.1113/JP282303. Epub 2022 Mar 9. J Physiol. 2022. PMID: 35194785
-
Activation of BK and SK channels by efferent synapses on outer hair cells in high-frequency regions of the rodent cochlea.J Neurosci. 2015 Feb 4;35(5):1821-30. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2790-14.2015. J Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 25653344 Free PMC article.
-
The multiple functions of T stellate/multipolar/chopper cells in the ventral cochlear nucleus.Hear Res. 2011 Jun;276(1-2):61-9. doi: 10.1016/j.heares.2010.10.018. Epub 2010 Nov 4. Hear Res. 2011. PMID: 21056098 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of synaptic signalling by postsynaptic, non-glutamate receptor ion channels.J Physiol. 2008 Mar 15;586(6):1475-80. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2007.148353. Epub 2007 Dec 20. J Physiol. 2008. PMID: 18096597 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Small molecule modulation of the large-conductance calcium-activated potassium channel suppresses salicylate-induced tinnitus in mice.Front Neurosci. 2022 Aug 25;16:763855. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2022.763855. eCollection 2022. Front Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 36090293 Free PMC article.
-
A novel BK channel-targeted peptide suppresses sound evoked activity in the mouse inferior colliculus.Sci Rep. 2017 Feb 14;7:42433. doi: 10.1038/srep42433. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28195225 Free PMC article.
-
The Na+ leak channel NALCN controls spontaneous activity and mediates synaptic modulation by α2-adrenergic receptors in auditory neurons.Elife. 2024 Jan 10;12:RP89520. doi: 10.7554/eLife.89520. Elife. 2024. PMID: 38197879 Free PMC article.
-
Quantitative distribution of choline acetyltransferase activity in rat trapezoid body.Hear Res. 2018 Dec;370:264-271. doi: 10.1016/j.heares.2018.08.008. Epub 2018 Aug 25. Hear Res. 2018. PMID: 30177425 Free PMC article.
-
Glutamate-activated BK channel complexes formed with NMDA receptors.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018 Sep 18;115(38):E9006-E9014. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1802567115. Epub 2018 Sep 4. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018. PMID: 30181277 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
