Ionotropic NMDA receptor signaling is required for the induction of long-term depression in the mouse hippocampal CA1 region
- PMID: 24719106
- PMCID: PMC3983804
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5419-13.2014
Ionotropic NMDA receptor signaling is required for the induction of long-term depression in the mouse hippocampal CA1 region
Abstract
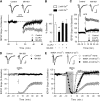
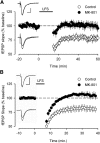
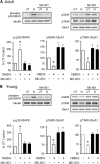
Previous studies have provided strong support for the notion that NMDAR-mediated increases in postsynaptic Ca(2+) have a crucial role in the induction of long-term depression (LTD). This view has recently been challenged, however, by findings suggesting that LTD induction is instead attributable to an ion channel-independent, metabotropic form of NMDAR signaling. Thus, to explore the role of ionotropic versus metabotropic NMDAR signaling in LTD, we examined the effects of varying extracellular Ca(2+) levels or blocking NMDAR channel ion fluxes with MK-801 on LTD and NMDAR signaling in the mouse hippocampal CA1 region. We find that the induction of LTD in the adult hippocampus is highly sensitive to extracellular Ca(2+) levels and that MK-801 blocks NMDAR-dependent LTD in the hippocampus of both adult and immature mice. Moreover, MK-801 inhibits NMDAR-mediated activation of p38-MAPK and dephosphorylation of AMPAR GluA1 subunits at sites implicated in LTD. Thus, our results indicate that the induction of LTD in the hippocampal CA1 region is dependent on ionotropic, rather than metabotropic, NMDAR signaling.
Keywords: MK-801; NMDA receptor; hippocampus; long-term depression.
Figures
References
-
- Chen X, Lin R, Chang L, Xu S, Wei X, Zhang J, Wang C, Anwyl R, Wang Q. Enhancement of long-term depression by soluble amyloid β protein in rat hippocampus is mediated by metabotropic glutamate receptor and involves activation of p38MAPK, STEP and caspase-3. Neuroscience. 2013;253:435–443. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2013.08.054. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
