Activation of spinal glucagon-like peptide-1 receptors specifically suppresses pain hypersensitivity
- PMID: 24719110
- PMCID: PMC6608999
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4703-13.2014
Activation of spinal glucagon-like peptide-1 receptors specifically suppresses pain hypersensitivity
Abstract
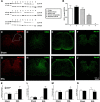
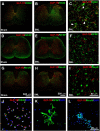
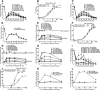
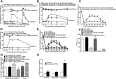
This study aims to identify the inhibitory role of the spinal glucagon like peptide-1 receptor (GLP-1R) signaling in pain hypersensitivity and its mechanism of action in rats and mice. First, GLP-1Rs were identified to be specifically expressed on microglial cells in the spinal dorsal horn, and profoundly upregulated after peripheral nerve injury. In addition, intrathecal GLP-1R agonists GLP-1(7-36) and exenatide potently alleviated formalin-, peripheral nerve injury-, bone cancer-, and diabetes-induced hypersensitivity states by 60-90%, without affecting acute nociceptive responses. The antihypersensitive effects of exenatide and GLP-1 were completely prevented by GLP-1R antagonism and GLP-1R gene knockdown. Furthermore, exenatide evoked β-endorphin release from both the spinal cord and cultured microglia. Exenatide antiallodynia was completely prevented by the microglial inhibitor minocycline, β-endorphin antiserum, and opioid receptor antagonist naloxone. Our results illustrate a novel spinal dorsal horn microglial GLP-1R/β-endorphin inhibitory pathway in a variety of pain hypersensitivity states.
Keywords: GLP-1 receptor; chronic pain; microglia.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Peptidic exenatide and herbal catalpol mediate neuroprotection via the hippocampal GLP-1 receptor/β-endorphin pathway.Pharmacol Res. 2015 Dec;102:276-85. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2015.10.008. Epub 2015 Nov 3. Pharmacol Res. 2015. PMID: 26546042
-
Microglial Activation of GLP-1R Signaling in Neuropathic Pain Promotes Gene Expression Adaption Involved in Inflammatory Responses.Neural Plast. 2021 Aug 31;2021:9923537. doi: 10.1155/2021/9923537. eCollection 2021. Neural Plast. 2021. PMID: 34512747 Free PMC article.
-
The non-peptide GLP-1 receptor agonist WB4-24 blocks inflammatory nociception by stimulating β-endorphin release from spinal microglia.Br J Pharmacol. 2015 Jan;172(1):64-79. doi: 10.1111/bph.12895. Epub 2014 Nov 24. Br J Pharmacol. 2015. PMID: 25176008 Free PMC article.
-
A review on the association between glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists and thyroid cancer.Exp Diabetes Res. 2012;2012:924168. doi: 10.1155/2012/924168. Epub 2012 May 28. Exp Diabetes Res. 2012. PMID: 22693487 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus with agonists of the GLP-1 receptor or DPP-IV inhibitors.Expert Opin Emerg Drugs. 2004 May;9(1):155-66. doi: 10.1517/eoed.9.1.155.32952. Expert Opin Emerg Drugs. 2004. PMID: 15155141 Review.
Cited by
-
New Advances on Pathophysiology of Diabetes Neuropathy and Pain Management: Potential Role of Melatonin and DPP-4 Inhibitors.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Apr 12;13:864088. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.864088. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35496279 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neuropeptides and Microglial Activation in Inflammation, Pain, and Neurodegenerative Diseases.Mediators Inflamm. 2017;2017:5048616. doi: 10.1155/2017/5048616. Epub 2017 Jan 5. Mediators Inflamm. 2017. PMID: 28154473 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Activation of Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptor Promotes Neuroprotection in Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis by Reducing Neuroinflammatory Responses.Mol Neurobiol. 2018 Apr;55(4):3007-3020. doi: 10.1007/s12035-017-0550-2. Epub 2017 Apr 29. Mol Neurobiol. 2018. PMID: 28456941
-
GLP-1 Receptor Agonists: Beyond Their Pancreatic Effects.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021 Aug 23;12:721135. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2021.721135. eCollection 2021. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021. PMID: 34497589 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A novel approach to treating opioid use disorders: Dual agonists of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptors and neuropeptide Y2 receptors.Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2021 Dec;131:1169-1179. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2021.10.026. Epub 2021 Oct 29. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2021. PMID: 34715149 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Alvarez E, Martínez MD, Roncero I, Chowen JA, García-Cuartero B, Gispert JD, Sanz C, Vázquez P, Maldonado A, de Cáceres J, Desco M, Pozo MA, Blázquez E. The expression of GLP-1 receptor mRNA and protein allows the effect of GLP-1 on glucose metabolism in the human hypothalamus and brainstem. J Neurochem. 2005;92:798–806. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2004.02914.x. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
