An internally modulated, thermostable, pH-sensitive Cys loop receptor from the hydrothermal vent worm Alvinella pompejana
- PMID: 24719323
- PMCID: PMC4031562
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M113.525576
An internally modulated, thermostable, pH-sensitive Cys loop receptor from the hydrothermal vent worm Alvinella pompejana
Abstract
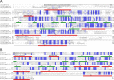
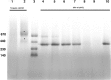
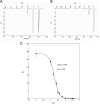
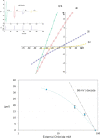
Cys loop receptors (CLRs) are commonly known as ligand-gated channels that transiently open upon binding of neurotransmitters to modify the membrane potential. However, a class of cation-selective bacterial homologues of CLRs have been found to open upon a sudden pH drop, suggesting further ligands and more functions of the homologues in prokaryotes. Here we report an anion-selective CLR from the hydrothermal vent annelid worm Alvinella pompejana that opens at low pH. A. pompejana expressed sequence tag databases were explored by us, and two full-length CLR sequences were identified, synthesized, cloned, expressed in Xenopus oocytes, and studied by two-electrode voltage clamp. One channel, named Alv-a1-pHCl, yielded functional receptors and opened upon a sudden pH drop but not by other known agonists. Sequence comparison showed that both CLR proteins share conserved characteristics with eukaryotic CLRs, such as an N-terminal helix, a cysteine loop motif, and an intracellular loop intermediate in length between the long loops of other eukaryotic CLRs and those of prokaryotic CLRs. Both full-length Alv-a1-pHCl and a truncated form, termed tAlv-a1-pHCl, lacking 37 amino-terminal residues that precede the N-terminal helix, formed functional channels in oocytes. After pH activation, tAlv-a1-pHCl showed desensitization and was not modulated by ivermectin. In contrast, pH-activated, full-length Alv-a1-pHCl showed a marked rebound current and was modulated significantly by ivermectin. A thermostability assay indicated that purified tAlv-a1-pHCl expressed in Sf9 cells denatured at a higher temperature than the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor from Torpedo californica.
Keywords: Alvinella pompejana; Cys Loop Receptor; Ivermectin; Membrane Proteins; Neurotransmitter Receptors; Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors; Patch Clamp Electrophysiology; Protein Conformation; Recombinant Protein Expression; pH Sensitivity.
© 2014 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Functional and Biochemical Characterization of Alvinella pompejana Cys-Loop Receptor Homologues.PLoS One. 2016 Mar 21;11(3):e0151183. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0151183. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 26999666 Free PMC article.
-
Modular design of Cys-loop ligand-gated ion channels: functional 5-HT3 and GABA rho1 receptors lacking the large cytoplasmic M3M4 loop.J Gen Physiol. 2008 Feb;131(2):137-46. doi: 10.1085/jgp.200709896. J Gen Physiol. 2008. PMID: 18227272 Free PMC article.
-
Phenylalanine in the pore of the Erwinia ligand-gated ion channel modulates picrotoxinin potency but not receptor function.Biochemistry. 2014 Oct 7;53(39):6183-8. doi: 10.1021/bi5008035. Epub 2014 Sep 19. Biochemistry. 2014. PMID: 25238029 Free PMC article.
-
Assembly of nicotinic and other Cys-loop receptors.J Neurochem. 2011 Mar;116(5):734-41. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2010.07060.x. Epub 2011 Jan 13. J Neurochem. 2011. PMID: 21214570 Review.
-
The structural basis of function in Cys-loop receptors.Q Rev Biophys. 2010 Nov;43(4):449-99. doi: 10.1017/S0033583510000168. Epub 2010 Sep 20. Q Rev Biophys. 2010. PMID: 20849671 Review.
Cited by
-
Sterol derivative binding to the orthosteric site causes conformational changes in an invertebrate Cys-loop receptor.Elife. 2023 Jul 3;12:e86029. doi: 10.7554/eLife.86029. Elife. 2023. PMID: 37395731 Free PMC article.
-
The atypical cation-conduction and gating properties of ELIC underscore the marked functional versatility of the pentameric ligand-gated ion-channel fold.J Gen Physiol. 2015 Jul;146(1):15-36. doi: 10.1085/jgp.201411333. Epub 2015 Jun 15. J Gen Physiol. 2015. PMID: 26078054 Free PMC article.
-
Functional and Biochemical Characterization of Alvinella pompejana Cys-Loop Receptor Homologues.PLoS One. 2016 Mar 21;11(3):e0151183. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0151183. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 26999666 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Corringer P.-J., Poitevin F., Prevost M. S., Sauguet L., Delarue M., Changeux J.-P. (2012) Structure and pharmacology of pentameric receptor channels: from bacteria to brain. Structure 20, 941–956 - PubMed
-
- Sine S. M., Engel A. G. (2006) Recent advances in Cys-loop receptor structure and function. Nature 440, 448–455 - PubMed
-
- Miyazawa A., Fujiyoshi Y., Unwin N. (2003) Structure and gating mechanism of the acetylcholine receptor pore. Nature 423, 949–955 - PubMed
-
- Karlin A. (2002) Emerging structure of the nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 3, 102–114 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

