The protein phosphatase 2A regulatory subunit B56γ mediates suppression of T cell receptor (TCR)-induced nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) activity
- PMID: 24719332
- PMCID: PMC4031550
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M113.533547
The protein phosphatase 2A regulatory subunit B56γ mediates suppression of T cell receptor (TCR)-induced nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) activity
Abstract
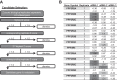
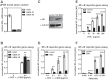
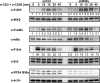
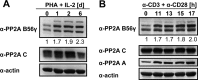
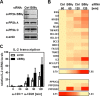
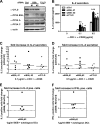
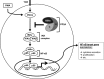
NF-κB is an important transcription factor in the immune system, and aberrant NF-κB activity contributes to malignant diseases and autoimmunity. In T cells, NF-κB is activated upon TCR stimulation, and signal transduction to NF-κB activation is triggered by a cascade of phosphorylation events. However, fine-tuning and termination of TCR signaling are only partially understood. Phosphatases oppose the role of kinases by removing phosphate moieties. The catalytic activity of the protein phosphatase PP2A has been implicated in the regulation of NF-κB. PP2A acts in trimeric complexes in which the catalytic subunit is promiscuous and the regulatory subunit confers substrate specificity. To understand and eventually target NF-κB-specific PP2A functions it is essential to define the regulatory PP2A subunit involved. So far, the regulatory PP2A subunit that mediates NF-κB suppression in T cells remained undefined. By performing a siRNA screen in Jurkat T cells harboring a NF-κB-responsive luciferase reporter, we identified the PP2A regulatory subunit B56γ as negative regulator of NF-κB in TCR signaling. B56γ was strongly up-regulated upon primary human T cell activation, and B56γ silencing induced increased IκB kinase (IKK) and IκBα phosphorylation upon TCR stimulation. B56γ silencing enhanced NF-κB activity, resulting in increased NF-κB target gene expression including the T cell cytokine IL-2. In addition, T cell proliferation was increased upon B56γ silencing. These data help to understand the physiology of PP2A function in T cells and the pathophysiology of diseases involving PP2A and NF-κB.
Keywords: B56γ; IL-2; NF-κB Transcription Factor; Nuclear Factor-κB (NF-κB); PPP2R5C; Phosphoprotein Phosphatase; Serine/Threonine Protein Phosphatase; Signaling; T Cell; T Cell Receptor.
© 2014 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

