The RNA-binding protein TDP-43 selectively disrupts microRNA-1/206 incorporation into the RNA-induced silencing complex
- PMID: 24719334
- PMCID: PMC4022891
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M114.561902
The RNA-binding protein TDP-43 selectively disrupts microRNA-1/206 incorporation into the RNA-induced silencing complex
Abstract
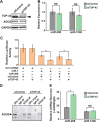
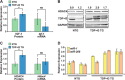
MicroRNA (miRNA) maturation is regulated by interaction of particular miRNA precursors with specific RNA-binding proteins. Following their biogenesis, mature miRNAs are incorporated into the RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC) where they interact with mRNAs to negatively regulate protein production. However, little is known about how mature miRNAs are regulated at the level of their activity. To address this, we screened for proteins differentially bound to the mature form of the miR-1 or miR-133 miRNA families. These muscle-enriched, co-transcribed miRNA pairs cooperate to suppress smooth muscle gene expression in the heart. However, they also have opposing roles, with the miR-1 family, composed of miR-1 and miR-206, promoting myogenic differentiation, whereas miR-133 maintains the progenitor state. Here, we describe a physical interaction between TDP-43, an RNA-binding protein that forms aggregates in the neuromuscular disease, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, and the miR-1, but not miR-133, family. Deficiency of the TDP-43 Drosophila ortholog enhanced dmiR-1 activity in vivo. In mammalian cells, TDP-43 limited the activity of both miR-1 and miR-206, but not the miR-133 family, by disrupting their RISC association. Consistent with TDP-43 dampening miR-1/206 activity, protein levels of the miR-1/206 targets, IGF-1 and HDAC4, were elevated in TDP-43 transgenic mouse muscle. This occurred without corresponding Igf-1 or Hdac4 mRNA increases and despite higher miR-1 and miR-206 expression. Our findings reveal that TDP-43 negatively regulates the activity of the miR-1 family of miRNAs by limiting their bioavailability for RISC loading and suggest a processing-independent mechanism for differential regulation of miRNA activity.
Keywords: Cardiac muscle; Gene Regulation; MicroRNA; RNA-Protein Interaction; RNA-binding Protein; Skeletal Muscle.
© 2014 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Structural determinants of miRNAs for RISC loading and slicer-independent unwinding.Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2009 Sep;16(9):953-60. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.1630. Epub 2009 Aug 16. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2009. PMID: 19684602
-
Multilayer checkpoints for microRNA authenticity during RISC assembly.EMBO Rep. 2011 Sep 1;12(9):944-9. doi: 10.1038/embor.2011.128. EMBO Rep. 2011. PMID: 21738221 Free PMC article.
-
The exoribonuclease Nibbler controls 3' end processing of microRNAs in Drosophila.Curr Biol. 2011 Nov 22;21(22):1888-93. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2011.10.006. Epub 2011 Nov 3. Curr Biol. 2011. PMID: 22055292 Free PMC article.
-
Intracellular and extracellular microRNA: An update on localization and biological role.Prog Histochem Cytochem. 2016 Nov;51(3-4):33-49. doi: 10.1016/j.proghi.2016.06.001. Epub 2016 Jun 25. Prog Histochem Cytochem. 2016. PMID: 27396686 Review.
-
Regulation of microRNA biogenesis and function.Thromb Haemost. 2012 Apr;107(4):605-10. doi: 10.1160/TH11-12-0836. Epub 2012 Feb 8. Thromb Haemost. 2012. PMID: 22318703 Review.
Cited by
-
A network of RNA and protein interactions in Fronto Temporal Dementia.Front Mol Neurosci. 2015 Mar 19;8:9. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2015.00009. eCollection 2015. Front Mol Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 25852467 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Expanding the TDP-43 Proteinopathy Pathway From Neurons to Muscle: Physiological and Pathophysiological Functions.Front Neurosci. 2022 Feb 3;16:815765. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2022.815765. eCollection 2022. Front Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35185458 Free PMC article. Review.
-
RNA Deregulation in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis: The Noncoding Perspective.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Sep 24;22(19):10285. doi: 10.3390/ijms221910285. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34638636 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mature miRNAs form secondary structure, which suggests their function beyond RISC.PLoS One. 2014 Nov 25;9(11):e113848. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0113848. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25423301 Free PMC article.
-
Role of RNA Binding Proteins with prion-like domains in muscle and neuromuscular diseases.Cell Stress. 2020 Mar 10;4(4):76-91. doi: 10.15698/cst2020.04.217. Cell Stress. 2020. PMID: 32292882 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Zhao Y., Samal E., Srivastava D. (2005) Serum response factor regulates a muscle-specific microRNA that targets Hand2 during cardiogenesis. Nature 436, 214–220 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

