SRC-1 and Twist1 expression positively correlates with a poor prognosis in human breast cancer
- PMID: 24719557
- PMCID: PMC3979992
- DOI: 10.7150/ijbs.8193
SRC-1 and Twist1 expression positively correlates with a poor prognosis in human breast cancer
Abstract
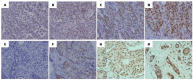
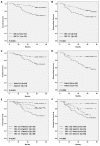
To evaluate the possible prognostic value of Steroid Receptor Coactivator-1 (SRC-1) and Twist1 expression in human breast cancer, we examined SRC-1 and Twist1 expression using immunohistochemistry on tissue microarray sections containing 137 breast cancer specimens. All patients were followed up for a median of 5 years following surgery. Survival curves were generated using the Kaplan-Meier method. Multivariate analysis was performed using the Cox proportional hazard regression model to assess the prognostic values. The results showed a positive correlation between SRC-1 and Twist1 expression at protein levels (P < 0.001). Also, SRC-1 expression positively correlated with HER2 expression (P = 0.024). The protein expression of Twist1 positively associated with lymph node metastasis (P < 0.001), but inversely correlated with PR status (P = 0.041). Patients with SRC-1 or Twist1-positive expression exhibited poorer overall survival (OS) and disease-free survival (DFS) than did those with SRC-1 or Twist1-negative expression (P < 0.05 for all). In addition, SRC-1-negativeive/Twist1-negative patients had the best OS and DFS (P < 0.01 for both). In multivariate survival analysis, SRC-1 expression, tumor stage, and PR were found to be independent prognostic factors related to OS (P = 0.019, < 0.001 and 0.02, respectively) and Twist1 expression, lymph node status and PR were independent predictors of DFS (P = 0.006, 0.001 and 0.029, respectively). These results suggest that a combined SRC-1/Twist1 expression status could improve the prognostic judgment for breast cancer patients.
Keywords: Breast cancer; Correlation; Prognosis.; SRC-1; Twist1.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
High SRC-1 and Twist1 expression predicts poor prognosis and promotes migration and invasion by inducing epithelial-mesenchymal transition in human nasopharyngeal carcinoma.PLoS One. 2019 Apr 11;14(4):e0215299. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0215299. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 30973923 Free PMC article.
-
High TWIST1 mRNA expression is associated with poor prognosis in lymph node-negative and estrogen receptor-positive human breast cancer and is co-expressed with stromal as well as ECM related genes.Breast Cancer Res. 2012 Sep 11;14(5):R123. doi: 10.1186/bcr3317. Breast Cancer Res. 2012. PMID: 22967435 Free PMC article.
-
Combined detection of Twist1, Snail1 and squamous cell carcinoma antigen for the prognostic evaluation of invasion and metastasis in cervical squamous cell carcinoma.Int J Clin Oncol. 2018 Apr;23(2):321-328. doi: 10.1007/s10147-017-1210-2. Epub 2017 Nov 3. Int J Clin Oncol. 2018. PMID: 29101499
-
ARTEMIN synergizes with TWIST1 to promote metastasis and poor survival outcome in patients with ER negative mammary carcinoma.Breast Cancer Res. 2011;13(6):R112. doi: 10.1186/bcr3054. Epub 2011 Nov 7. Breast Cancer Res. 2011. PMID: 22060274 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic significance of hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha, TWIST1 and Snail expression in resectable non-small cell lung cancer.Thorax. 2009 Dec;64(12):1082-9. doi: 10.1136/thx.2009.115691. Epub 2009 Sep 23. Thorax. 2009. PMID: 19778933 Review.
Cited by
-
Sp1 and COX2 expression is positively correlated with a poor prognosis in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma.Oncotarget. 2016 May 10;7(19):28207-17. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.8593. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27057636 Free PMC article.
-
A Novel Mouse Model for SNP in Steroid Receptor Co-Activator-1 Reveals Role in Bone Density and Breast Cancer Metastasis.Endocrinology. 2021 Aug 1;162(8):bqab094. doi: 10.1210/endocr/bqab094. Endocrinology. 2021. PMID: 33963375 Free PMC article.
-
Steroid receptor coactivator 1 promotes human hepatocellular carcinoma invasiveness through enhancing MMP-9.J Cell Mol Med. 2024 Apr;28(7):e18171. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.18171. J Cell Mol Med. 2024. PMID: 38506084 Free PMC article.
-
Relationship between circulating tumor cells and epithelial to mesenchymal transition in early breast cancer.BMC Cancer. 2015 Jul 22;15:533. doi: 10.1186/s12885-015-1548-7. BMC Cancer. 2015. PMID: 26194471 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical implications of the coexpression of SRC1 and NANOG in HER-2-overexpressing breast cancers.Onco Targets Ther. 2016 Sep 6;9:5483-8. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S102386. eCollection 2016. Onco Targets Ther. 2016. PMID: 27660465 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Xu J, Qiu Y, DeMayo FJ, Tsai SY, Tsai MJ, O'Malley BW. Partial hormone resistance in mice with disruption of the steroid receptor coactivator-1 (SRC-1) gene. Science. 1998;279:1922–5. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

