Amelioration of stroke-induced neurological deficiency by lyophilized powder of catapol and puerarin
- PMID: 24719562
- PMCID: PMC3979997
- DOI: 10.7150/ijbs.8571
Amelioration of stroke-induced neurological deficiency by lyophilized powder of catapol and puerarin
Abstract
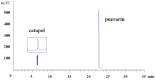
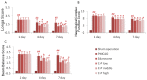
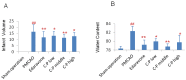
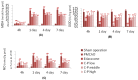
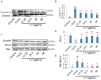
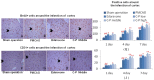
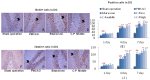
Catalpol and puerarin are active ingredients isolated from Rehmannia glutinosa Libosch and Radix Puerariae, respectively. They are popular in research for their poly-pharmacological effects. This research focused on effect of anti-stroke by lyophilized powder of catalpol and puerarin (C-P) and potential mechanisms. At the beginning of research, C-P was identified and analyzed by HPLC. Neurological function was evaluated by Longa score, neurological complex function score and beam balance score after permanent middle cerebral artery occlusion (PMCAO) in mice. Infarct volume and water content were evaluated after treatment of C-P. Anti-oxidative stress, anti-apoptosis, angiogenesis and neurogenesis were investigated by ELISA, WB and immunohistochemical stain respectively. With treatment of C-P, neurological deficiency of PMCAO mice was ameliorated. Morphologically, infarct volume and water content in ischemic hemisphere were significantly reduced by C-P. In vivo and in vitro, oxidative stress injury was extenuated by C-P. Meanwhile, Caspase-3 was down-regulated and Bxl-2 was up-regulated by C-P in vivo. In addition, C-P enhanced angiogenesis around the infarct of cortex and neurogenesis in the Hippocampal Dentate Gyrus (DG). Hence, C-P ameliorated stroke-induced neurological deficiency through its multiple neuroprotections. What's more, this article provides us a novel formula of active ingredients for stroke.
Keywords: catapol; neurological function.; puerarin; stroke.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Lyophilized Powder of Catalpol and Puerarin Protected Cerebral Vessels from Ischemia by Its Anti-apoptosis on Endothelial Cells.Int J Biol Sci. 2017 Feb 25;13(3):327-338. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.17751. eCollection 2017. Int J Biol Sci. 2017. PMID: 28367097 Free PMC article.
-
Lyophilized Powder of Catalpol and Puerarin Protects Neurovascular Unit from Stroke.Int J Biol Sci. 2016 Jan 28;12(4):367-80. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.14059. eCollection 2016. Int J Biol Sci. 2016. PMID: 27019622 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of delayed puerarin treatment in long-term neurological outcomes of focal ischemic stroke in rats.Indian J Pharmacol. 2014 Mar-Apr;46(2):157-60. doi: 10.4103/0253-7613.129305. Indian J Pharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24741185 Free PMC article.
-
Puerarin provides a neuroprotection against transient cerebral ischemia by attenuating autophagy at the ischemic penumbra in neurons but not in astrocytes.Neurosci Lett. 2017 Mar 16;643:45-51. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2017.02.009. Epub 2017 Feb 10. Neurosci Lett. 2017. PMID: 28192195
-
Neuroprotection of Catalpol for Experimental Acute Focal Ischemic Stroke: Preclinical Evidence and Possible Mechanisms of Antioxidation, Anti-Inflammation, and Antiapoptosis.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2017;2017:5058609. doi: 10.1155/2017/5058609. Epub 2017 Jul 13. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2017. PMID: 28785376 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Catalpol Enhances Neurogenesis And Inhibits Apoptosis Of New Neurons Via BDNF, But Not The BDNF/Trkb Pathway.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2019 Dec 10;13:4145-4157. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S223322. eCollection 2019. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2019. PMID: 31849446 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Puerarin on the Prevention and Treatment of Cardiovascular Diseases.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Dec 7;12:771793. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.771793. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34950032 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Catalpol Protects Against Retinal Ischemia Through Antioxidation, Anti-Ischemia, Downregulation of β-Catenin, VEGF, and Angiopoietin-2: In Vitro and In Vivo Studies.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Apr 24;26(9):4019. doi: 10.3390/ijms26094019. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40362263 Free PMC article.
-
Knockdown of HIF-1α impairs post-ischemic vascular reconstruction in the brain via deficient homing and sprouting bmEPCs.Brain Pathol. 2018 Nov;28(6):860-874. doi: 10.1111/bpa.12628. Epub 2018 Oct 9. Brain Pathol. 2018. PMID: 30052311 Free PMC article.
-
Development of an Oral Compound Pickering Emulsion Composed of Nanocrystals of Poorly Soluble Ingredient and Volatile Oils from Traditional Chinese Medicine.Pharmaceutics. 2018 Oct 1;10(4):170. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics10040170. Pharmaceutics. 2018. PMID: 30275390 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Diener HC, Katsarava Z, Weimar C. Headache associated with ischemiccerebrovascular disease. Rev. Neurol. (Paris) 2008;164(10):819–824. - PubMed
-
- Candelario-Jalil E. Injury and repair mechanisms in ischemic stroke: considerations for the development of novel neurotherapeutics. Current opinion in investigational drugs (London, England: 2000) 2009;10(7):644–654. - PubMed
-
- Chan PH. Role of oxidants in ischemic brain damage. Stroke. 1996;27(6):1124–1129. - PubMed
-
- Harold P. et al. Guidelines for the early management of patients with ischemic stroke a scientific statement from the stroke council of the american stroke association. Stroke. 2003;(34):1056–1083. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

