Electroacupuncture promotes proliferation of amplifying neural progenitors and preserves quiescent neural progenitors from apoptosis to alleviate depressive-like and anxiety-like behaviours
- PMID: 24719647
- PMCID: PMC3955608
- DOI: 10.1155/2014/872568
Electroacupuncture promotes proliferation of amplifying neural progenitors and preserves quiescent neural progenitors from apoptosis to alleviate depressive-like and anxiety-like behaviours
Abstract
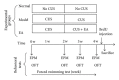
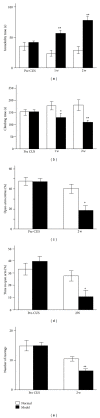
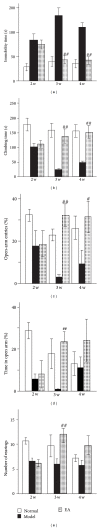
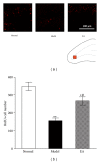
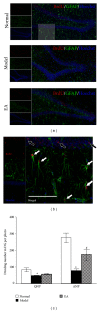
The present study was designed to investigate the effects of electroacupuncture (EA) on depressive-like and anxiety-like behaviours and neural progenitors in the hippocampal dentate gyrus (DG) in a chronic unpredictable stress (CUS) rat model of depression. After being exposed to a CUS procedure for 2 weeks, rats were subjected to EA treatment, which was performed on acupoints Du-20 (Bai-Hui) and GB-34 (Yang-Ling-Quan), once every other day for 15 consecutive days (including 8 treatments), with each treatment lasting for 30 min. The behavioural tests (i.e., forced swimming test, elevated plus-maze test, and open-field entries test) revealed that EA alleviated the depressive-like and anxiety-like behaviours of the stressed rats. Immunohistochemical results showed that proliferative cells (BrdU-positive) in the EA group were significantly larger in number compared with the Model group. Further, the results showed that EA significantly promoted the proliferation of amplifying neural progenitors (ANPs) and simultaneously inhibited the apoptosis of quiescent neural progenitors (QNPs). In a word, the mechanism underlying the antidepressant-like effects of EA is associated with enhancement of ANPs proliferation and preserving QNPs from apoptosis.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Electro-Acupuncture Alleviates Chronic Unpredictable Stress-Induced Depressive- and Anxiety-Like Behavior and Hippocampal Neuroinflammation in Rat Model of Depression.Front Mol Neurosci. 2018 May 31;11:149. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2018.00149. eCollection 2018. Front Mol Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 29946236 Free PMC article.
-
Electroacupuncture upregulates ERK signaling pathways and promotes adult hippocampal neural progenitors proliferation in a rat model of depression.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2013 Oct 28;13:288. doi: 10.1186/1472-6882-13-288. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2013. PMID: 24165147 Free PMC article.
-
Electroacupuncture attenuates the decrease of hippocampal progenitor cell proliferation in the adult rats exposed to chronic unpredictable stress.Life Sci. 2007 Nov 10;81(21-22):1489-95. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2007.08.033. Epub 2007 Sep 12. Life Sci. 2007. PMID: 17976657
-
Effects of chronic electroacupuncture on depression- and anxiety-like behaviors in rats with chronic neuropathic pain.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2014;2014:158987. doi: 10.1155/2014/158987. Epub 2014 Mar 26. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2014. PMID: 24795763 Free PMC article.
-
Electroacupuncture combined with clomipramine enhances antidepressant effect in rodents.Neurosci Lett. 2007 Jun 21;421(1):5-9. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2007.02.052. Epub 2007 Feb 24. Neurosci Lett. 2007. PMID: 17548153
Cited by
-
Effects of Electroacupuncture on Chronic Unpredictable Mild Stress Rats Depression-Like Behavior and Expression of p-ERK/ERK and p-P38/P38.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2015;2015:650729. doi: 10.1155/2015/650729. Epub 2015 Aug 20. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2015. PMID: 26366182 Free PMC article.
-
Electro-Acupuncture Alleviates Chronic Unpredictable Stress-Induced Depressive- and Anxiety-Like Behavior and Hippocampal Neuroinflammation in Rat Model of Depression.Front Mol Neurosci. 2018 May 31;11:149. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2018.00149. eCollection 2018. Front Mol Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 29946236 Free PMC article.
-
Acupuncture: Emerging evidence for its use as an analgesic (Review).Exp Ther Med. 2015 May;9(5):1577-1581. doi: 10.3892/etm.2015.2348. Epub 2015 Mar 12. Exp Ther Med. 2015. PMID: 26136861 Free PMC article.
-
Electroacupuncture Mechanisms in Managing Preoperative Anxiety and Postoperative Pain Chronification: A Review.J Pain Res. 2024 Dec 4;17:4089-4100. doi: 10.2147/JPR.S498373. eCollection 2024. J Pain Res. 2024. PMID: 39650212 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Modulation of Acupuncture on Cell Apoptosis and Autophagy.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2017;2017:8268736. doi: 10.1155/2017/8268736. Epub 2017 Nov 27. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2017. PMID: 29279719 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kaptchuk TJ. Acupuncture: theory, efficacy, and practice. Annals of Internal Medicine. 2002;136(5):374–383. - PubMed
-
- Mirescu C, Gould E. Stress and adult neurogenesis. Hippocampus. 2006;16(3):233–238. - PubMed
-
- Mukaino Y, Park J, White A, Ernst E. The effectiveness of acupuncture for depression—a systematic review of randomised controlled trials. Acupuncture in Medicine. 2005;23(2):70–76. - PubMed
-
- Liu Q, Yu J, Mi W-L, et al. Electroacupuncture attenuates the decrease of hippocampal progenitor cell proliferation in the adult rats exposed to chronic unpredictable stress. Life Sciences. 2007;81(21-22):1489–1495. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

