Resolving Vitamin D Deficiency in the Preconception Period among High-Risk Reproductive Women: A Randomized Controlled Trial
- PMID: 24719700
- PMCID: PMC3964418
- DOI: 10.5812/ircmj.11175
Resolving Vitamin D Deficiency in the Preconception Period among High-Risk Reproductive Women: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Abstract
Background: Although vitamin D deficiency has been linked to potential complications in reproductive women, the recommended intake dosage of this vitamin in populations with high incidence of deficiency in preconception period has not been defined.
Objectives: The study investigated the effect of consuming a dosage of 2000 IU/day oral vitamin D for 105 days, on serum levels of this vitamin in reproductive women.
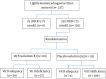
Materials and methods: 229 women with 18-35 years old, who were confirmed to be vitamin D deficient (vitamin D < 75 nmol/L), were randomized into the intervention and control groups and after 15 weeks consumption of the supplement and placebo, their serum samples were obtained.
Results: At baseline the mean serum levels of vitamin D in the control group was 23.34 ± 15.87 nmol/L and in intervention group was 25.13 ± 18.46 nmol/L, that these values didn't have any significant difference (P = 0.43), while after intervention, significant differences between the two groups was noticed (P < 0.001). The affecting factors to achieve normal range of vitamin D in the intervention group included basal amounts of vitamin D and two underlying factors based on questionnaire data: use of oral supplements (except vitamin D and calcium) in daily life and perfect sun exposure.
Conclusion: This study showed positive effect of the 2000 IU/day oral vitamin D on the serum level elevation of this vitamin in reproductive women.
Keywords: Dietary Supplements; Preconception; Vitamin D Deficiency.
Figures
References
-
- Alagol F, Shihadeh Y, Boztepe H, Tanakol R, Yarman S, Azizlerli H, et al. Sunlight exposure and vitamin D deficiency in Turkish women. J Endocrinol Invest. 2000;23(3):173–7. - PubMed
-
- Mishal AA. Effects of different dress styles on vitamin D levels in healthy young Jordanian women. Osteoporos Int. 2001;12(11):931–5. - PubMed
-
- Namgung R, Tsang RC. Bone in the pregnant mother and newborn at birth. Clin Chim Acta. 2003;333(1):1–11. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources