Prunus yedoensis bark inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory cytokine synthesis by IκBα degradation and MAPK activation in macrophages
- PMID: 24720857
- PMCID: PMC3993036
- DOI: 10.1089/jmf.2013.2825
Prunus yedoensis bark inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory cytokine synthesis by IκBα degradation and MAPK activation in macrophages
Abstract
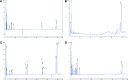
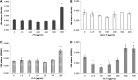
The bark of Prunus yedoensis is used in antitussive medicines and in oral herbal formulations for inflammatory skin disorders. In the present study, we explored whether P. yedoensis bark extract (PYE) and its solvent partitioned fractions could modulate lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α and interleukin (IL)-6 in vivo and in vitro. In addition, we examined the effect of PYE extract and its fractions on LPS-induced NF-κB and mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling in mouse peritoneal macrophages. Oral treatment of PYE decreased serum levels of TNF-α and IL-6 in LPS injected mice. PYE inhibited LPS-induced TNF-α and IL-6 in macrophages at the transcriptional level and also suppressed LPS-induced IκBα degradation and MAPK activation in vitro. Among the fractions, the chloroform fraction, which contains genistein, naringenin, sakuranetin, prunetin, and amygdalin, showed inhibitory effects at much lower concentrations than the water and ethyl acetate fractions. Taken together, our results indicate that PYE was able to inhibit LPS-induced expression of TNF-α and IL-6, the latter of which was more prominent. The effects of PYE on inflammatory cytokine synthesis may involve modulation of NF-κB and MAPK activation.
Figures




References
-
- Matsuoka N, Ikeda T, El-Aasr M,Manabe H, Murakami Y, Deguchi H, Nohara T: Study of the chemical constituents of Pruni Cortex and its related parts. J Nat Med 2011;65:166–171 - PubMed
-
- Jung HA, Kim AR, Chung HY, Choi JS: In vitro antioxidant activity of some selected Prunus species in Korea. Arch Pharm Res 2002;25:865–872 - PubMed
-
- Jo K, Lee SE, Lee SW, Hwang JK: Prunus yedoensis Matsum. stimulates glucose uptake in L6 rat skeletal muscle cells by activating AMP-activated protein kinase and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt pathways. Nat Prod Res 2012;26:1610–1615 - PubMed
-
- Kang GJ, Lee HJ, Yoon WJ, Yang EJ, Park SS, Kang HK, Park MH, Yoo ES: Prunus yedoensis inhibits the inflammatory chemokines, MDC and TARC, by regulating the STAT1-signaling pathway in IFN-g-stimulated HaCaT human keratinocytes. Biomol Ther 2008;16:394–402
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

