Nitrite treatment rescues cardiac dysfunction in aged mice treated with conjugated linoleic acid
- PMID: 24721151
- PMCID: PMC4108078
- DOI: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2014.03.043
Nitrite treatment rescues cardiac dysfunction in aged mice treated with conjugated linoleic acid
Abstract
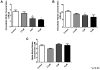
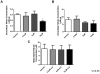
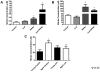
Conjugated linoleic acid (cLA) is a commercially available weight-loss supplement that is not currently regulated by the U.S. FDA. Numerous studies suggest that cLA mediates protection against diseases including cancer, diabetes, atherosclerosis, immune function, and obesity. Based upon these reports, it was hypothesized that supplementation with cLA would improve heart function in aged wild-type (WT) mice. At 10 months of age, mice were treated with cLA, nitrite, or the combination of the two. Echocardiograms revealed that cardiac function was decreased in aged compared to young WT mice, as determined by percentage of fractional shortening. Also, contrary to the hypothesis, mice that received cLA (6-week treatment) had significantly worse cardiac function compared to controls. This effect was attenuated when mice were cotreated with cLA and nitrite. Taken together, these results suggest that cLA-mediated cardiac injury can be circumvented by nitrite supplementation in a murine model of aging.
Keywords: Conjugated linoleic acid; Free radicals; Heart function; Nitrite; eNOS.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures







References
-
- Mele MC, Cannelli G, Carta G, Cordeddu L, Melis MP, Murru E, Stanton C, Banni S. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids. 2013;89:115–119. - PubMed
-
- Kelley NS, Hubbard NE, Erickson KL. J Nutr. 2007;137:2599–2607. - PubMed
-
- Mooney D, McCarthy C, Belton O. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2012;98:56–62. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

