X-exome sequencing in Finnish families with intellectual disability--four novel mutations and two novel syndromic phenotypes
- PMID: 24721225
- PMCID: PMC4022384
- DOI: 10.1186/1750-1172-9-49
X-exome sequencing in Finnish families with intellectual disability--four novel mutations and two novel syndromic phenotypes
Abstract
Background: X-linked intellectual disability (XLID) is a group of genetically heterogeneous disorders characterized by substantial impairment in cognitive abilities, social and behavioral adaptive skills. Next generation sequencing technologies have become a powerful approach for identifying molecular gene mutations relevant for diagnosis.
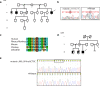
Methods & objectives: Enrichment of X-chromosome specific exons and massively parallel sequencing was performed for identifying the causative mutations in 14 Finnish families, each of them having several males affected with intellectual disability of unknown cause.
Results: We found four novel mutations in known XLID genes. Two mutations; one previously reported missense mutation (c.1111C > T), and one novel frameshift mutation (c. 990_991insGCTGC) were identified in SLC16A2, a gene that has been linked to Allan-Herndon-Dudley syndrome (AHDS). One novel missense mutation (c.1888G > C) was found in GRIA3 and two novel splice donor site mutations (c.357 + 1G > C and c.985 + 1G > C) were identified in the DLG3 gene. One missense mutation (c.1321C > T) was identified in the candidate gene ZMYM3 in three affected males with a previously unrecognized syndrome characterized by unique facial features, aortic stenosis and hypospadia was detected. All of the identified mutations segregated in the corresponding families and were absent in > 100 Finnish controls and in the publicly available databases. In addition, a previously reported benign variant (c.877G > A) in SYP was identified in a large family with nine affected males in three generations, who have a syndromic phenotype.
Conclusions: All of the mutations found in this study are being reported for the first time in Finnish families with several affected male patients whose etiological diagnoses have remained unknown to us, in some families, for more than 30 years. This study illustrates the impact of X-exome sequencing to identify rare gene mutations and the challenges of interpreting the results. Further functional studies are required to confirm the cause of the syndromic phenotypes associated with ZMYM3 and SYP in this study.
Figures




References
-
- Schalok RL, Borthwick-Duffy SA, Bradley VJ, Buntinx WHE, Coulter DL, Craig EM, Gomez SC, Reeve A, Shogren KA, Snell ME, Spreat S, Tasse MJ, Thompson JR, Verdugo-Alonso MA, Yeager MH. AAIDD’s 11th edition of Intellectual Disability: Definition, Classification, and Systems of Support. 2012.
-
- de Brouwer AP, Yntema HG, Kleefstra T, Lugtenberg D, Oudakker AR, de Vries BB, van Bokhoven H, Van Esch H, Frints SG, Froyen G, Fryns JP, Raynaud M, Moizard MP, Ronce N, Bensalem A, Moraine C, Poirier K, Castelnau L, Saillour Y, Bienvenu T, Beldjord C, des Portes V, Chelly J, Turner G, Fullston T, Gecz J, Kuss AW, Tzschach A, Jensen LR, Lenzner S. et al.Mutation frequencies of X-linked mental retardation genes in families from the EuroMRX consortium. Hum Mutat. 2007;28:207–208. - PubMed
-
- Willemsen M, Kleefstra T. Making headaway with genetic diagnostics of intellectual disabilities. Clin Genet. 2013;85:101–110. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

