Effects of frequent hemodialysis on perceived caregiver burden in the Frequent Hemodialysis Network trials
- PMID: 24721892
- PMCID: PMC4011443
- DOI: 10.2215/CJN.07170713
Effects of frequent hemodialysis on perceived caregiver burden in the Frequent Hemodialysis Network trials
Abstract
Background and objectives: Patients receiving hemodialysis often perceive their caregivers are overburdened. We hypothesize that increasing hemodialysis frequency would result in higher patient perceptions of burden on their unpaid caregivers.
Design, setting, participants, & measurements: In two separate trials, 245 patients were randomized to receive in-center daily hemodialysis (6 days/week) or conventional hemodialysis (3 days/week) while 87 patients were randomized to receive home nocturnal hemodialysis (6 nights/week) or home conventional hemodialysis for 12 months. Changes in overall mean scores over time in the 10-question Cousineau perceived burden scale were compared.
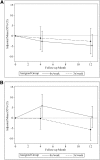
Results: In total, 173 of 245 (70%) and 80 of 87 (92%) randomized patients in the Daily and Nocturnal Trials, respectively, reported having an unpaid caregiver at baseline or during follow-up. Relative to in-center conventional dialysis, the 12-month change in mean perceived burden score with in-center daily hemodialysis was -2.1 (95% confidence interval, -9.4 to +5.3; P=0.58). Relative to home conventional dialysis, the 12-month change in mean perceived burden score with home nocturnal dialysis was +6.1 (95% confidence interval, -0.8 to +13.1; P=0.08). After multiple imputation for missing data in the Nocturnal Trial, the relative difference between home nocturnal and home conventional hemodialysis was +9.4 (95% confidence interval, +0.55 to +18.3; P=0.04). In the Nocturnal Trial, changes in perceived burden were inversely correlated with adherence to dialysis treatments (Pearson r=-0.35; P=0.02).
Conclusion: Relative to conventional hemodialysis, in-center daily hemodialysis did not result in higher perceptions of caregiver burden. There was a trend to higher perceived caregiver burden among patients randomized to home nocturnal hemodialysis. These findings may have implications for the adoption of and adherence to frequent nocturnal hemodialysis.
Keywords: daily hemodialysis; outcomes; randomized controlled trials.
Figures
Comment in
-
Caregiver burden and hemodialysis.Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2014 May;9(5):840-2. doi: 10.2215/CJN.02690314. Epub 2014 Apr 10. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2014. PMID: 24721889 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Burden on caregivers as perceived by hemodialysis patients in the Frequent Hemodialysis Network (FHN) trials.Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2011 Jul;26(7):2316-22. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfr007. Epub 2011 Mar 18. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2011. PMID: 21421590 Free PMC article.
-
Cognitive changes associated with switching to frequent nocturnal hemodialysis or renal transplantation.BMC Nephrol. 2016 Jan 22;17:12. doi: 10.1186/s12882-016-0223-9. BMC Nephrol. 2016. PMID: 26801094 Free PMC article.
-
Patients receiving frequent hemodialysis have better health-related quality of life compared to patients receiving conventional hemodialysis.Kidney Int. 2017 Mar;91(3):746-754. doi: 10.1016/j.kint.2016.10.033. Epub 2017 Jan 13. Kidney Int. 2017. PMID: 28094031 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Nocturnal hemodialysis: an underutilized modality?Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2018 Nov;27(6):472-477. doi: 10.1097/MNH.0000000000000450. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2018. PMID: 30281539 Review.
-
Intensive Hemodialysis and Potential Risks With Increasing Treatment.Am J Kidney Dis. 2016 Nov;68(5S1):S51-S58. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2016.05.020. Am J Kidney Dis. 2016. PMID: 27772644 Review.
Cited by
-
The Relationship Between Care Burden and Coping Strategies in Caregivers of Hemodialysis Patients in Kermanshah, Iran.Psychol Res Behav Manag. 2020 Feb 5;13:133-140. doi: 10.2147/PRBM.S233103. eCollection 2020. Psychol Res Behav Manag. 2020. PMID: 32104113 Free PMC article.
-
The Potential Burden of Home Dialysis on Patients and Caregivers: A Narrative Review.Can J Kidney Health Dis. 2019 Dec 18;6:2054358119893335. doi: 10.1177/2054358119893335. eCollection 2019. Can J Kidney Health Dis. 2019. PMID: 31897304 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Home hemodialysis technique survival: insights and challenges.BMC Nephrol. 2023 Jul 11;24(1):205. doi: 10.1186/s12882-023-03264-5. BMC Nephrol. 2023. PMID: 37434110 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Quality of life in primary caregivers of patients in peritoneal dialysis and hemodialysis.J Bras Nefrol. 2021 Oct-Dec;43(4):486-494. doi: 10.1590/2175-8239-JBN-2020-0229. J Bras Nefrol. 2021. PMID: 34096964 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of the teach-back method on caregiver outcomes using the "Timing it Right" framework for hemodialysis patients.Front Public Health. 2023 Jun 23;11:1123006. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2023.1123006. eCollection 2023. Front Public Health. 2023. PMID: 37427278 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Suri RS, Garg AX, Chertow GM, Levin NW, Rocco MV, Greene T, Beck GJ, Gassman JJ, Eggers PW, Star RA, Ornt DB, Kliger AS, Frequent Hemodialysis Network Trial Group : Frequent Hemodialysis Network (FHN) randomized trials: Study design. Kidney Int 71: 349–359, 2007 - PubMed
-
- Chertow GM, Levin NW, Beck GJ, Depner TA, Eggers PW, Gassman JJ, Gorodetskaya I, Greene T, James S, Larive B, Lindsay RM, Mehta RL, Miller B, Ornt DB, Rajagopalan S, Rastogi A, Rocco MV, Schiller B, Sergeyeva O, Schulman G, Ting GO, Unruh ML, Star RA, Kliger AS, FHN Trial Group : In-center hemodialysis six times per week versus three times per week. N Engl J Med 363: 2287–2300, 2010 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Rocco MV, Lockridge RS, Jr., Beck GJ, Eggers PW, Gassman JJ, Greene T, Larive B, Chan CT, Chertow GM, Copland M, Hoy CD, Lindsay RM, Levin NW, Ornt DB, Pierratos A, Pipkin MF, Rajagopalan S, Stokes JB, Unruh ML, Star RA, Kliger AS, Kliger A, Eggers P, Briggs J, Hostetter T, Narva A, Star R, Augustine B, Mohr P, Beck G, Fu Z, Gassman J, Greene T, Daugirdas J, Hunsicker L, Larive B, Li M, Mackrell J, Wiggins K, Sherer S, Weiss B, Rajagopalan S, Sanz J, Dellagrottaglie S, Kariisa M, Tran T, West J, Unruh M, Keene R, Schlarb J, Chan C, McGrath-Chong M, Frome R, Higgins H, Ke S, Mandaci O, Owens C, Snell C, Eknoyan G, Appel L, Cheung A, Derse A, Kramer C, Geller N, Grimm R, Henderson L, Prichard S, Roecker E, Rocco M, Miller B, Riley J, Schuessler R, Lockridge R, Pipkin M, Peterson C, Hoy C, Fensterer A, Steigerwald D, Stokes J, Somers D, Hilkin A, Lilli K, Wallace W, Franzwa B, Waterman E, Chan C, McGrath-Chong M, Copland M, Levin A, Sioson L, Cabezon E, Kwan S, Roger D, Lindsay R, Suri R, Champagne J, Bullas R, Garg A, Mazzorato A, Spanner E, Rocco M, Burkart J, Moossavi S, Mauck V, Kaufman T, Pierratos A, Chan W, Regozo K, Kwok S, Frequent Hemodialysis Network (FHN) Trial Group : The effects of frequent nocturnal home hemodialysis: The Frequent Hemodialysis Network Nocturnal Trial. Kidney Int 80: 1080–1091, 2011 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

