Interplay of the serine/threonine-kinase StkP and the paralogs DivIVA and GpsB in pneumococcal cell elongation and division
- PMID: 24722178
- PMCID: PMC3983041
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1004275
Interplay of the serine/threonine-kinase StkP and the paralogs DivIVA and GpsB in pneumococcal cell elongation and division
Abstract
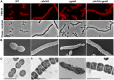
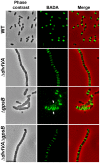
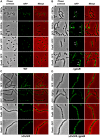
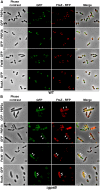
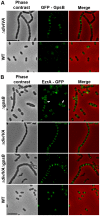
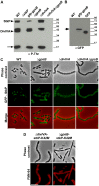
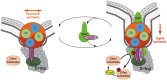
Despite years of intensive research, much remains to be discovered to understand the regulatory networks coordinating bacterial cell growth and division. The mechanisms by which Streptococcus pneumoniae achieves its characteristic ellipsoid-cell shape remain largely unknown. In this study, we analyzed the interplay of the cell division paralogs DivIVA and GpsB with the ser/thr kinase StkP. We observed that the deletion of divIVA hindered cell elongation and resulted in cell shortening and rounding. By contrast, the absence of GpsB resulted in hampered cell division and triggered cell elongation. Remarkably, ΔgpsB elongated cells exhibited a helical FtsZ pattern instead of a Z-ring, accompanied by helical patterns for DivIVA and peptidoglycan synthesis. Strikingly, divIVA deletion suppressed the elongated phenotype of ΔgpsB cells. These data suggest that DivIVA promotes cell elongation and that GpsB counteracts it. Analysis of protein-protein interactions revealed that GpsB and DivIVA do not interact with FtsZ but with the cell division protein EzrA, which itself interacts with FtsZ. In addition, GpsB interacts directly with DivIVA. These results are consistent with DivIVA and GpsB acting as a molecular switch to orchestrate peripheral and septal PG synthesis and connecting them with the Z-ring via EzrA. The cellular co-localization of the transpeptidases PBP2x and PBP2b as well as the lipid-flippases FtsW and RodA in ΔgpsB cells further suggest the existence of a single large PG assembly complex. Finally, we show that GpsB is required for septal localization and kinase activity of StkP, and therefore for StkP-dependent phosphorylation of DivIVA. Altogether, we propose that the StkP/DivIVA/GpsB triad finely tunes the two modes of peptidoglycan (peripheral and septal) synthesis responsible for the pneumococcal ellipsoid cell shape.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Suppression and synthetic-lethal genetic relationships of ΔgpsB mutations indicate that GpsB mediates protein phosphorylation and penicillin-binding protein interactions in Streptococcus pneumoniae D39.Mol Microbiol. 2017 Mar;103(6):931-957. doi: 10.1111/mmi.13613. Epub 2017 Feb 7. Mol Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28010038 Free PMC article.
-
GpsB Coordinates StkP Signaling as a PASTA Kinase Adaptor in Streptococcus pneumoniae Cell Division.J Mol Biol. 2024 Nov 15;436(22):168797. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2024.168797. Epub 2024 Sep 19. J Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 39303764
-
Requirement of essential Pbp2x and GpsB for septal ring closure in Streptococcus pneumoniae D39.Mol Microbiol. 2013 Dec;90(5):939-55. doi: 10.1111/mmi.12408. Epub 2013 Oct 17. Mol Microbiol. 2013. PMID: 24118410 Free PMC article.
-
Structural basis for interaction of DivIVA/GpsB proteins with their ligands.Mol Microbiol. 2019 Jun;111(6):1404-1415. doi: 10.1111/mmi.14244. Epub 2019 Apr 2. Mol Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 30887576 Review.
-
Cell division of Streptococcus pneumoniae: think positive!Curr Opin Microbiol. 2016 Dec;34:18-23. doi: 10.1016/j.mib.2016.07.014. Epub 2016 Aug 4. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 27497051 Review.
Cited by
-
Illumination of growth, division and secretion by metabolic labeling of the bacterial cell surface.FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2015 Mar;39(2):184-202. doi: 10.1093/femsre/fuu012. Epub 2015 Jan 23. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2015. PMID: 25725012 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Control of Morphological Differentiation of Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2) by Phosphorylation of MreC and PBP2.PLoS One. 2015 Apr 30;10(4):e0125425. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0125425. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25927987 Free PMC article.
-
Negative regulation of MurZ and MurA underlies the essentiality of GpsB- and StkP-mediated protein phosphorylation in Streptococcus pneumoniae D39.Mol Microbiol. 2023 Sep;120(3):351-383. doi: 10.1111/mmi.15122. Epub 2023 Jul 14. Mol Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37452010 Free PMC article.
-
Giving a signal: how protein phosphorylation helps Bacillus navigate through different life stages.FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2023 Jul 5;47(4):fuad044. doi: 10.1093/femsre/fuad044. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2023. PMID: 37533212 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Phosphorylation-dependent activation of the cell wall synthase PBP2a in Streptococcus pneumoniae by MacP.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018 Mar 13;115(11):2812-2817. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1715218115. Epub 2018 Feb 27. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018. PMID: 29487215 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Egan AJ, Vollmer W (2012) The physiology of bacterial cell division. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences 1277: 8–28. - PubMed
-
- Cabeen MT, Jacobs-Wagner C (2010) The bacterial cytoskeleton. Annual review of genetics 44: 365–392. - PubMed
-
- Flardh K (2010) Cell polarity and the control of apical growth in Streptomyces . Current opinion in microbiology 13: 758–765. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

