Competitive virus and host RNAs: the interplay of a hidden virus and host interaction
- PMID: 24723323
- PMCID: PMC3996157
- DOI: 10.1007/s13238-014-0039-y
Competitive virus and host RNAs: the interplay of a hidden virus and host interaction
Abstract
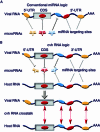
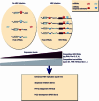
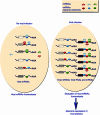
During virus infection, viral RNAs and mRNAs function as blueprints for viral protein synthesis and possibly as pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) in innate immunity. Here, considering recent research progress in microRNAs (miRNAs) and competitive endogenous RNAs (ceRNAs), we speculate that viral RNAs act as sponges and can sequester endogenous miRNAs within infected cells, thus cross-regulating the stability and translational efficiency of host mRNAs with shared miRNA response elements. This cross-talk and these reciprocal interactions between viral RNAs and host mRNAs are termed "competitive viral and host RNAs" (cvhRNAs). We further provide recent experimental evidence for the existence of cvhRNAs networks in hepatitis B virus (HBV), as well as Herpesvirus saimiri (HVS), lytic murine cytomegalovirus (MCMV) and human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) infections. In addition, the cvhRNA hypothesis also predicts possible cross-regulation between host and other viruses, such as hepatitis C virus (HCV), HIV, influenza virus, human papillomaviruses (HPV). Since the interaction between miRNAs and viral RNAs also inevitably leads to repression of viral RNA function, we speculate that virus may evolve either to employ cvhRNA networks or to avoid miRNA targeting for optimal fitness within the host. CvhRNA networks may therefore play a fundamental role in the regulation of viral replication, infection establishment, and viral pathogenesis.
Figures
References
-
- Ala U, Karreth FA, Bosia C, Pagnani A, Taulli R, Léopold V, Tay Y, Provero P, Zecchina R, Pandolfi PP. Integrated transcriptional and competitive endogenous RNA networks are cross-regulated in permissive molecular environments. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2013;110:7154–7159. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1222509110. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

